The long non-coding RNA BC200 (BCYRN1) is critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation
- PMID: 28651607
- PMCID: PMC5483959
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0679-7
The long non-coding RNA BC200 (BCYRN1) is critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation
Abstract
Background: BC200 is a long non-coding RNA expressed at high levels in the brain and elevated in a variety of tumour types. BC200 has a hypothesized role in translational regulation; however, to date the functional role of BC200 in both normal and diseased states remains poorly characterized.
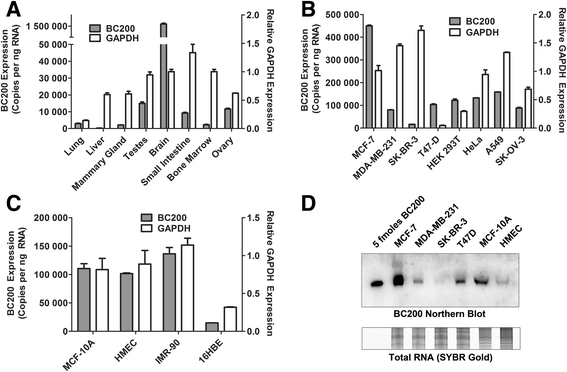
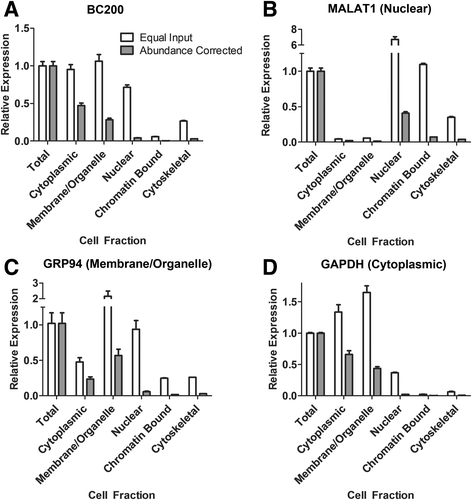
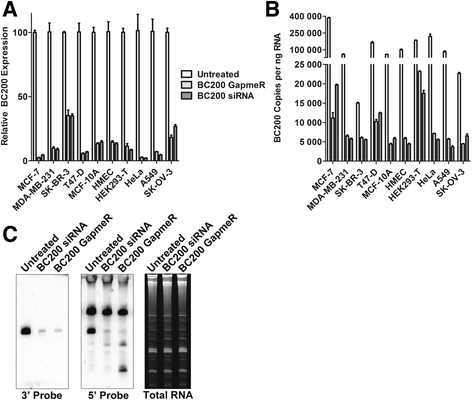
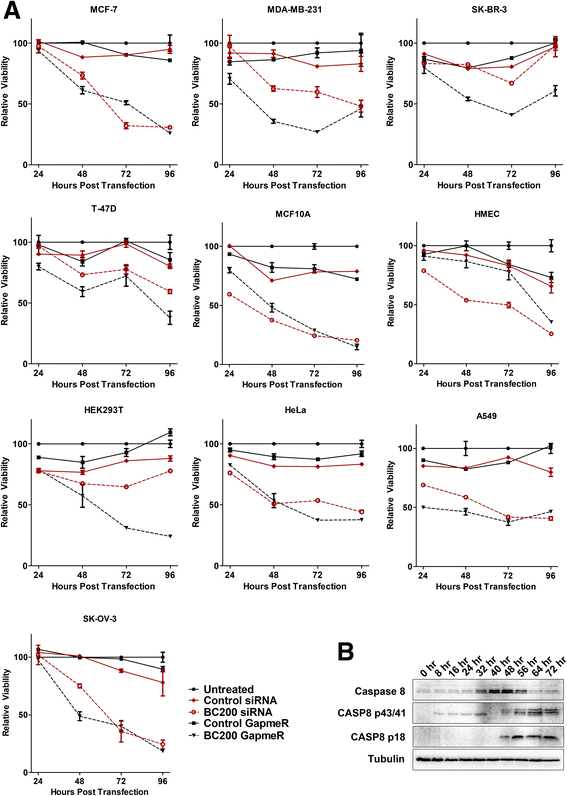
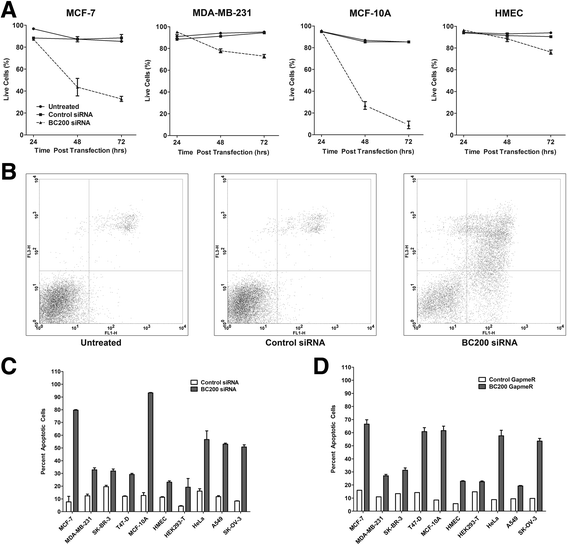
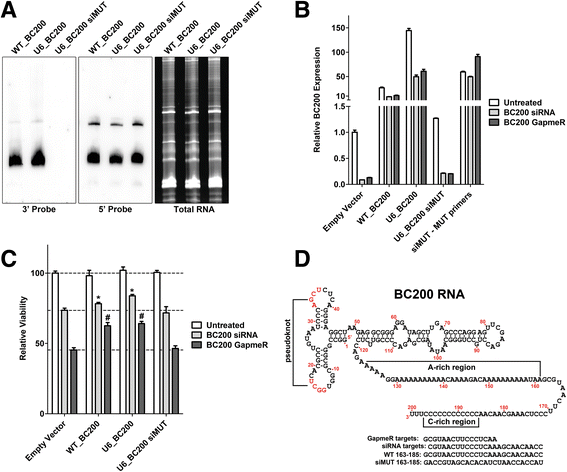
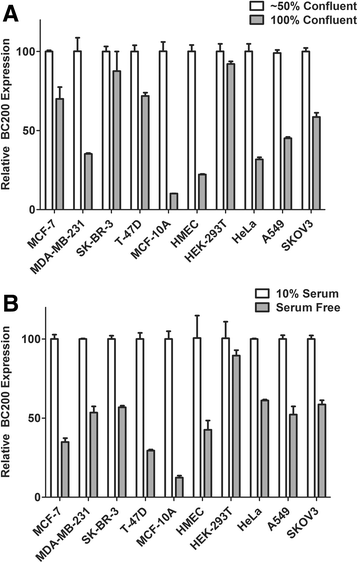
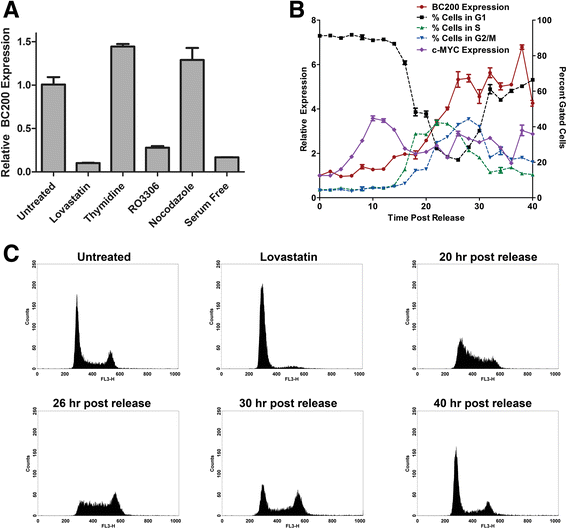
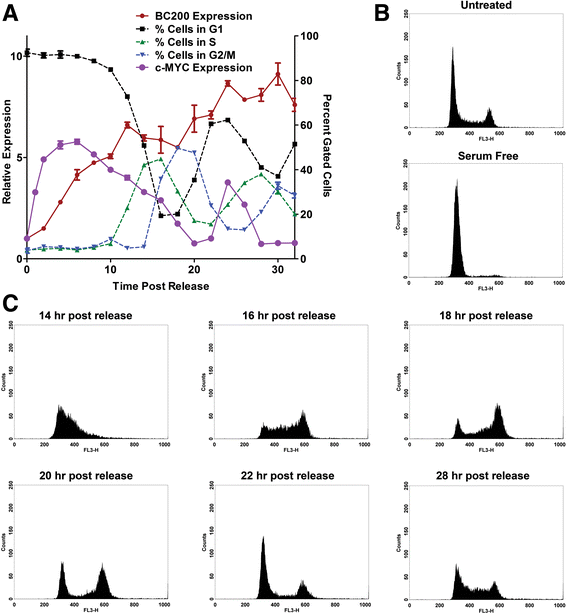
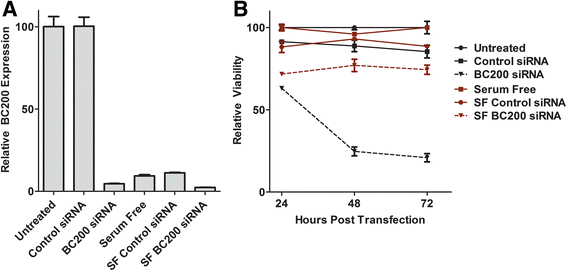
Methods: Detailed BC200 expression analyses were performed in tumor cell lines, primary and non-tumorigenic cultured breast and lung cells, and a panel of normal human tissues by quantitative real-time PCR and confirmed by northern blot. Subcellular fractionation was performed to assess BC200 distribution and efficient knock-down of BC200 was established using both locked nucleic acid (LNA) GapmeRs and conventional siRNAs. Cell viability following BC200 knockdown and overexpression was assessed by MTT assay and induction of apoptosis was monitored by Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry. Cell cycle arrest and synchronization were performed using serum withdrawal as well as the specific inhibitors Lovastatin, Thymidine, RO3306 and Nocodazole. Synchronization was monitored by fluorescent analysis of cellular DNA content by flow cytometry RESULTS: BC200 expression was substantially upregulated in brain and elevated expression was also observed in testes, small intestine and ovary. Expression in cultured tumour cells was dramatically higher than corresponding normal tissue; however, expression in cultured primary cells was similar to that in immortalized and cancer cell lines. BC200 knockdown resulted in a dramatic loss of viability through growth arrest and induction of apoptosis that could be partially rescued by overexpression of wild-type BC200 but not an siRNA-resistant sequence mutant. A substantial decrease in BC200 expression was observed upon cell confluence or serum deprivation, as well as drug induced cell cycle arrest in G1 or G2 but not S- or M-phases. Upon release from cell cycle arrest, BC200 expression was recovered as cells entered S-phase, but did not follow a periodic expression pattern during synchronized progression through the cell cycle. This elevated expression was critical for the survival of proliferating cancerous and non-cancerous cells, but is dispensable upon senescence or cell cycle arrest.
Conclusions: BC200 expression is elevated in proliferating cultured cells regardless of origin. In primary cells, expression is dramatically reduced upon cell cycle arrest by confluence, serum deprivation or chemical inhibition. The lethality of BC200 knockdown is restricted to actively proliferating cells, making it a promising therapeutic target for a broad spectrum of cancers.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BC200; BCYRN1; Cancer; Cell cycle; Cell proliferation; Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA); Viability.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

