Optimisation of a double-centrifugation method for preparation of canine platelet-rich plasma
- PMID: 28651609
- PMCID: PMC5485745
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-017-1123-3
Optimisation of a double-centrifugation method for preparation of canine platelet-rich plasma
Abstract
Background: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been expected for regenerative medicine because of its growth factors. However, there is considerable variability in the recovery and yield of platelets and the concentration of growth factors in PRP preparations. The aim of this study was to identify optimal relative centrifugal force and spin time for the preparation of PRP from canine blood using a double-centrifugation tube method.
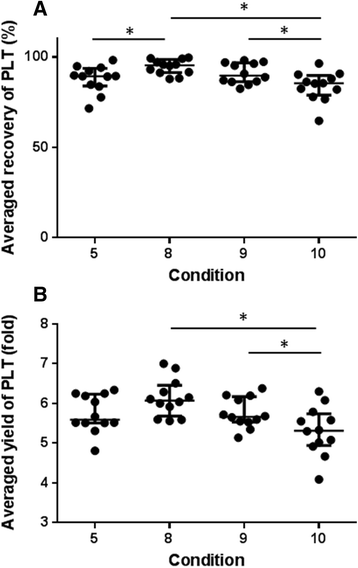
Methods: Whole blood samples were collected in citrate blood collection tubes from 12 healthy beagles. For the first centrifugation step, 10 different run conditions were compared to determine which condition produced optimal recovery of platelets. Once the optimal condition was identified, platelet-containing plasma prepared using that condition was subjected to a second centrifugation to pellet platelets. For the second centrifugation, 12 different run conditions were compared to identify the centrifugal force and spin time to produce maximal pellet recovery and concentration increase. Growth factor levels were estimated by using ELISA to measure platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) concentrations in optimised CaCl2-activated platelet fractions.
Results: The highest platelet recovery rate and yield were obtained by first centrifuging whole blood at 1000 g for 5 min and then centrifuging the recovered platelet-enriched plasma at 1500 g for 15 min. This protocol recovered 80% of platelets from whole blood and increased platelet concentration six-fold and produced the highest concentration of PDGF-BB in activated fractions.
Conclusions: We have described an optimised double-centrifugation tube method for the preparation of PRP from canine blood. This optimised method does not require particularly expensive equipment or high technical ability and can readily be carried out in a veterinary clinical setting.
Keywords: Dog; Double centrifugation; Platelet recovery; Platelet-derived growth factor-BB; Platelet-rich plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
This manuscript is part of a MS thesis submitted by Dr. Shin to the College of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental dogs were housed at Kangwon National University (Chuncheon, Korea) in compliance with guidelines outlined by the Kangwon National University Animal Care Committee. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kangwon National University (Korea), Approval no.: KNU-160511-1.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Kaplan DR, Chao FC, Stiles CD, Antoniades HN, Scher CD. Platelet alpha granules contain a growth factor for fibroblasts. Blood. 1979;53(6):1043–1052. - PubMed
-
- Assoian RK, Komoriya A, Meyers CA, Miller DM, Sporn MB. Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983;258(11):7155–7160. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

