Synthetic Cyclic Peptomers as Type III Secretion System Inhibitors
- PMID: 28652236
- PMCID: PMC5571333
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00060-17
Synthetic Cyclic Peptomers as Type III Secretion System Inhibitors
Abstract
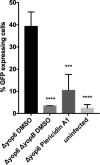
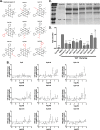
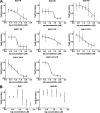
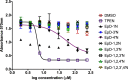
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are an emerging threat to global public health. New classes of antibiotics and tools for antimicrobial discovery are urgently needed. Type III secretion systems (T3SS), which are required by dozens of Gram-negative bacteria for virulence but largely absent from nonpathogenic bacteria, are promising virulence blocker targets. The ability of mammalian cells to recognize the presence of a functional T3SS and trigger NF-κB activation provides a rapid and sensitive method for identifying chemical inhibitors of T3SS activity. In this study, we generated a HEK293 stable cell line expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) driven by a promoter containing NF-κB enhancer elements to serve as a readout of T3SS function. We identified a family of synthetic cyclic peptide-peptoid hybrid molecules (peptomers) that exhibited dose-dependent inhibition of T3SS effector secretion in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa without affecting bacterial growth or motility. Among these inhibitors, EpD-3'N, EpD-1,2N, EpD-1,3'N, EpD-1,2,3'N, and EpD-1,2,4'N exhibited strong inhibitory effects on translocation of the Yersinia YopM effector protein into mammalian cells (>40% translocation inhibition at 7.5 μM) and showed no toxicity to mammalian cells at 240 μM. In addition, EpD-3'N and EpD-1,2,4'N reduced the rounding of HeLa cells caused by the activity of Yersinia effector proteins that target the actin cytoskeleton. In summary, we have discovered a family of novel cyclic peptomers that inhibit the injectisome T3SS but not the flagellar T3SS.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; T3SS; Yersinia; cyclic peptides; peptoids; peptomers; type III secretion system; virulence blocker.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

