Characterization of the Activities of Dinuclear Thiolato-Bridged Arene Ruthenium Complexes against Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 28652238
- PMCID: PMC5571360
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01031-17
Characterization of the Activities of Dinuclear Thiolato-Bridged Arene Ruthenium Complexes against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
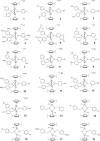
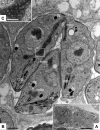
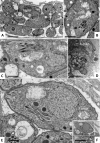
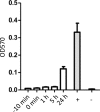
The in vitro effects of 18 dinuclear thiolato-bridged arene ruthenium complexes (1 monohiolato compound, 4 dithiolato compounds, and 13 trithiolato compounds), originally designed as anticancer agents, on the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii grown in human foreskin fibroblast (HFF) host cells were studied. Some trithiolato compounds exhibited antiparasitic efficacy at concentrations of 250 nM and below. Among those, complex 1 and complex 2 inhibited T. gondii proliferation with 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of 34 and 62 nM, respectively, and they did not affect HFFs at dosages of 200 μM or above, resulting in selectivity indices of >23,000. The IC50s of complex 9 were 1.2 nM for T. gondii and above 5 μM for HFFs. Transmission electron microscopy detected ultrastructural alterations in the matrix of the parasite mitochondria at the early stages of treatment, followed by a more pronounced destruction of tachyzoites. However, none of the three compounds applied at 250 nM for 15 days was parasiticidal. By affinity chromatography using complex 9 coupled to epoxy-activated Sepharose followed by mass spectrometry, T. gondii translation elongation factor 1α and two ribosomal proteins, RPS18 and RPL27, were identified to be potential binding proteins. In conclusion, organometallic ruthenium complexes exhibit promising activities against Toxoplasma, and the potential mechanisms of action of these compounds as well as their prospective applications for the treatment of toxoplasmosis are discussed.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; affinity chromatography; electron microscopy; in vitro culture; mitochondrion; ruthenium complex; toxoplasmosis; translation elongation factor 1α.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular and Molecular Targets of Nucleotide-Tagged Trithiolato-Bridged Arene Ruthenium Complexes in the Protozoan Parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma brucei.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 5;22(19):10787. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910787. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639127 Free PMC article.
-
The quest of the best - A SAR study of trithiolato-bridged dinuclear Ruthenium(II)-Arene compounds presenting antiparasitic properties.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 15;222:113610. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113610. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34144354
-
Targeting of the mitochondrion by dinuclear thiolato-bridged arene ruthenium complexes in cancer cells and in the apicomplexan parasite Neospora caninum.Metallomics. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):462-474. doi: 10.1039/c8mt00307f. Metallomics. 2019. PMID: 30620038
-
Recent progress on anti-Toxoplasma drugs discovery: Design, synthesis and screening.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 1;183:111711. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111711. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31585276 Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia: a review of published RCTs.Parasitol Res. 2017 Jul;116(7):1793-1799. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5478-y. Epub 2017 May 15. Parasitol Res. 2017. PMID: 28508166 Review.
Cited by
-
Coumarin-Tagged Dinuclear Trithiolato-Bridged Ruthenium(II)⋅Arene Complexes: Photophysical Properties and Antiparasitic Activity.Chembiochem. 2020 Oct 1;21(19):2818-2835. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000174. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Chembiochem. 2020. PMID: 32347622 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Antiparasitic Activity of Novel BPZ Derivatives Against Toxoplasma gondii.Microorganisms. 2020 Jul 30;8(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081159. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32751616 Free PMC article.
-
Unifying Virulence Evaluation in Toxoplasma gondii: A Timely Task.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 28;12:868727. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.868727. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35573788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Activities of MMV Malaria Box Compounds against the Apicomplexan Parasite Neospora caninum, the Causative Agent of Neosporosis in Animals.Molecules. 2020 Mar 24;25(6):1460. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061460. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32213892 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Targets of Nucleotide-Tagged Trithiolato-Bridged Arene Ruthenium Complexes in the Protozoan Parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma brucei.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 5;22(19):10787. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910787. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ronconi L, Sadler PJ. 2007. Using coordination chemistry to design new medicines. Coord Chem Rev 251:1633–1648. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

