Neurogenic pulmonary oedema: a rare cause of maternal collapse
- PMID: 28652270
- PMCID: PMC5534767
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-217375
Neurogenic pulmonary oedema: a rare cause of maternal collapse
Abstract
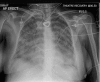
Acute pulmonary oedema is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in pregnant and postpartum women. We present an unusual case of near-fatal acute pulmonary oedema in a pregnant woman, which was attributed to the acute onset of neurogenic pulmonary oedema secondary to epileptic seizure activity. The patient required supportive management in the intensive care setting for a short period and subsequently made complete recovery with regular neurological follow-up arranged for the management of her epilepsy.
2017 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sciscone AC, Ivester T, Largoza M, et al. Acute pulmonary edema in pregnancy. Obstet Gynaecol 2003;101:511–5. - PubMed
-
- Knight M, Tuffnell D, Kenyon S, et al. on behalf of MBRRACE-UK. Saving Lives, Improving Mothers’ Care—surveillance of maternal deaths in the UK 2011–13 and lessons learned to inform maternity care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2009–13. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, University of Oxford, 2015. https//www.npeu.ox.ac.uk/mbrrace-uk/reports
-
- Dennis AT, Solnordal BC. Acute pulmonary oedema in pregnancy. Aneasthesia 2012;67:646–59. - PubMed
-
- Shanahan WT. Acute pulmonary edema as a complication of epileptic seizures. N Y Med J 1908;87:54–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical