Both MisR (CpxR) and MisS (CpxA) Are Required for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Infection in a Murine Model of Lower Genital Tract Infection
- PMID: 28652307
- PMCID: PMC5563589
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00307-17
Both MisR (CpxR) and MisS (CpxA) Are Required for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Infection in a Murine Model of Lower Genital Tract Infection
Abstract
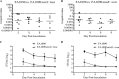
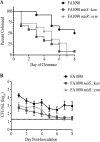
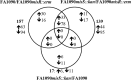
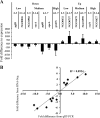
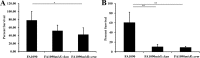
During infection, Neisseria gonorrhoeae senses and responds to stress; such responses may be modulated by MisRS (NGO0177 and NGO0176), a two-component system that is a homolog of CpxRA. In Escherichia coli, CpxRA senses and responds to envelope stress; CpxA is a sensor kinase/phosphatase for CpxR, a response regulator. When a cpxA mutant is grown in medium containing glucose, CpxR is phosphorylated by acetyl phosphate but cannot be dephosphorylated, resulting in constitutive activation. Kandler and coworkers (J. L. Kandler, C. L. Holley, J. L. Reimche, V. Dhulipala, J. T. Balthazar, A. Muszyński, R. W. Carlson, and W. M. Shafer, Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:4690-4700, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00823-16) showed that MisR (CpxR) is required for the maintenance of membrane integrity and resistance to antimicrobial peptides, suggesting a role in gonococcal survival in vivo Here, we evaluated the contributions of MisR and MisS (CpxA) to gonococcal infection in a murine model of cervicovaginal colonization and identified MisR-regulated genes using RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq). The deletion of misR or misS severely reduced the capacity of N. gonorrhoeae to colonize mice or maintain infection over a 7-day period and reduced microbial fitness after exposure to heat shock. Compared to the wild type (WT), the inactivation of misR identified 157 differentially regulated genes, most of which encoded putative envelope proteins. The inactivation of misS identified 17 differentially regulated genes compared to the WT and 139 differentially regulated genes compared to the misR mutant, 111 of which overlapped those differentially expressed in the comparison of the WT versus the misR mutant. These data indicate that an intact MisRS system is required for gonococcal infection of mice. Provided the MisR is constitutively phosphorylated in the misS mutant, the data suggest that controlled but not constitutive activation is required for gonococcal infection in mice.
Keywords: CpxRA; MisRS; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; RNA-Seq; envelope stress; genes; infection; mice.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of CpxRA as a Therapeutic Target for Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infections.Infect Immun. 2018 Feb 20;86(3):e00798-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00798-17. Print 2018 Mar. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29311237 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of CpxRA in Haemophilus ducreyi primarily inhibits the expression of its targets, including major virulence determinants.J Bacteriol. 2013 Aug;195(15):3486-502. doi: 10.1128/JB.00372-13. Epub 2013 May 31. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23729647 Free PMC article.
-
CpxA Phosphatase Inhibitor Activates CpxRA and Is a Potential Treatment for Uropathogenic Escherichia coli in a Murine Model of Infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0243021. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02430-21. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35297652 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanisms used by Neisseria gonorrhoeae to initiate infection differ between men and women.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004 Oct;17(4):965-81, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.4.965-981.2004. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15489357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ironclad truth: how in vivo transcriptomics and in vitro mechanistic studies shape our understanding of Neisseria gonorrhoeae gene regulation during mucosal infection.Pathog Dis. 2017 Jul 31;75(5):ftx057. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftx057. Pathog Dis. 2017. PMID: 28520925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Cpx envelope stress system contributes to transcriptional activation of rovM.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):37-57. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1556151. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 30518290 Free PMC article.
-
Global Network Analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Identifies Coordination between Pathways, Processes, and Regulators Expressed during Human Infection.mSystems. 2020 Feb 4;5(1):e00729-19. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00729-19. mSystems. 2020. PMID: 32019834 Free PMC article.
-
Cpx-signalling in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis modulates Lipid-A remodelling and resistance to last-resort antimicrobials.NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2024;2(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s44259-024-00059-y. Epub 2024 Nov 18. NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2024. PMID: 39568730 Free PMC article.
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Exposed to Sublethal Levels of Hydrogen Peroxide Mounts a Complex Transcriptional Response.mSystems. 2018 Oct 2;3(5):e00156-18. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00156-18. eCollection 2018 Sep-Oct. mSystems. 2018. PMID: 30320218 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the female reproductive tract: neutrophilic host response, sustained infection, and clinical sequelae.Curr Opin Hematol. 2018 Jan;25(1):13-21. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000394. Curr Opin Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29016383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hook EW, Handsfield HH. 2008. Gonococcal infection in the adult, p 627–645. In Holmes KK. (ed), Sexually transmitted diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
-
- Cohen MS, Hoffman RA, Royce RA, Kazembe P, Dyer JR, Daly CC, Zimba D, Vernazza PL, Maida M, Fiscus SA, Eron JJJ. 1997. Reduction of concentration of HIV-1 in semen after treatment of urethritis: implications for prevention of sexual transmission of HIV-1. Lancet 349:1868–1873. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)02190-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

