Cryo-EM structure of the DNA-PK holoenzyme
- PMID: 28652322
- PMCID: PMC5514765
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1707386114
Cryo-EM structure of the DNA-PK holoenzyme
Abstract
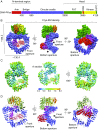
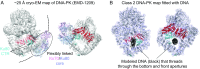
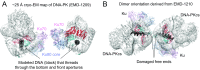
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a large protein complex central to the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA-repair pathway. It comprises the DNA-PK catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and the heterodimer of DNA-binding proteins Ku70 and Ku80. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human DNA-PKcs at 4.4-Å resolution and the DNA-PK holoenzyme at 5.8-Å resolution. The DNA-PKcs structure contains three distinct segments: the N-terminal region with an arm and a bridge, the circular cradle, and the head that includes the kinase domain. Two perpendicular apertures exist in the structure, which are sufficiently large for the passage of dsDNA. The DNA-PK holoenzyme cryo-EM map reveals density for the C-terminal globular domain of Ku80 that interacts with the arm of DNA-PKcs. The Ku80-binding site is adjacent to the previously identified density for the DNA-binding region of the Ku70/Ku80 complex, suggesting concerted DNA interaction by DNA-PKcs and the Ku complex.
Keywords: DNA repair; NHEJ; V(D)J recombination; cryo-EM; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: Signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat Genet. 2001;27:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Downs JA, Jackson SP. A means to a DNA end: The many roles of Ku. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:367–378. - PubMed
-
- Smith GC, Jackson SP. The DNA-dependent protein kinase. Genes Dev. 1999;13:916–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

