Diagnostic Accuracy of PIVKA-II, Alpha-Fetoprotein and a Combination of both in Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Affected by Chronic HCV Infection
- PMID: 28652441
- PMCID: PMC5566924
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11115
Diagnostic Accuracy of PIVKA-II, Alpha-Fetoprotein and a Combination of both in Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Affected by Chronic HCV Infection
Abstract
Background/aim: Patients affected by liver cirrhosis are at high risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of PIVKA-II (protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II) alone or in combination with α-1 fetoprotein (AFP), as a screening marker for development of HCC.
Materials and methods: A case-control study was conducted in 2 hospital wards in Naples. All anti-HCV-positive patients affected by HCC were considered as cases, while consecutive anti-HCV-positive patients without HCC were considered as controls.
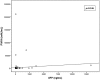
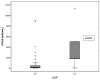
Results: Overall, 160 patients were enrolled, 56 cases and 104 controls. At the set cut-off of 36 mAU/ml, PIVKA-II was more sensitive (78.6% vs. 60%), but less specific than AFP at the set cut-off of 12 ng/ml (66.3% vs. 77.2%). The negative predictive value of PIVKA in combination with AFP was 93.2%.
Conclusion: PIVKA II, when combined with AFP, may be considered as a screening test for HCC due to its high negative predictive value.
Keywords: AFP; Cirrhosis; HCC; HCV; PIVKA-II.
Copyright© 2017, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- WHO GUIDELINES FOR THE SCREENING, CARE AND TREATMENT OF PERSONS WITH HEPATITIS C INFECTION. WHO. 2014 - PubMed
-
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver , European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer EASL–EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–943. - PubMed
-
- Ertle JM, Heider D, Wichert M, Keller B, Kueper R, Hilgard P, Gerken G, Schlaak JF. A Combination of a-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin is superior in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion. 2013;87(2):121–131. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
