Discovery of long-range inhibitory signaling to ensure single axon formation
- PMID: 28652571
- PMCID: PMC5484694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00044-2
Discovery of long-range inhibitory signaling to ensure single axon formation
Abstract
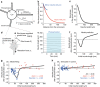
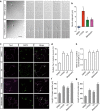
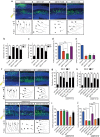
A long-standing question in neurodevelopment is how neurons develop a single axon and multiple dendrites from common immature neurites. Long-range inhibitory signaling from the growing axon is hypothesized to prevent outgrowth of other immature neurites and to differentiate them into dendrites, but the existence and nature of this inhibitory signaling remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that axonal growth triggered by neurotrophin-3 remotely inhibits neurite outgrowth through long-range Ca2+ waves, which are delivered from the growing axon to the cell body. These Ca2+ waves increase RhoA activity in the cell body through calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. Optogenetic control of Rho-kinase combined with computational modeling reveals that active Rho-kinase diffuses to growing other immature neurites and inhibits their outgrowth. Mechanistically, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I phosphorylates a RhoA-specific GEF, GEF-H1, whose phosphorylation enhances its GEF activity. Thus, our results reveal that long-range inhibitory signaling mediated by Ca2+ wave is responsible for neuronal polarization.Emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota influences immune function in the brain and may play a role in neurological diseases. Here, the authors offer in vivo evidence from a Drosophila model that supports a role for gut microbiota in modulating the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

