Zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced atherosclerotic alterations in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 28652743
- PMCID: PMC5476650
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S134897
Zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced atherosclerotic alterations in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
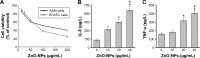
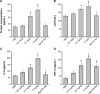
Engineered zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are currently being produced in high tonnage. Exposure to ZnO-NPs presents potential risks to cardiovascular system. Thus far, the toxicological effects of ZnO-NPs on cardiovascular system have not been well characterized. In this study, human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) were exposed to ZnO-NPs directly or indirectly using a transwell coculture system with human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 to mimic the lung/circulation interaction. It was shown that levels of proinflammatory mediators (interleukin-8 [IL-8] and tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]) and biomarkers of atherosclerogenesis (heme oxygenase-1 [HO-1] and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecules-1 [PECAM-1]) in the supernatants of culture media were significantly increased. Pretreatment of A549 cells on the apical side of the coculture system with the phagocytosis inhibitor cytochalasin B (CB) blocked ZnO-NP-induced HO-1 and PECAM-1 expression in HCAEC, indicating that endocytosis of ZnO-NPs by alveolar epithelial cells was involved in ZnO-NP-induced HO-1 or PECAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Moreover, Wistar rats were intratracheally instilled with ZnO-NP suspension and high fat diet (positive control). ZnO-NP treatment induced lung and systemic inflammation, dyslipidemia, increased levels of serum HO-1 and PECAM-1, and aortic pathological damage. Taken together, exposure to ZnO-NPs could induce atherosclerotic alterations, which might involve phagocytosis of nanoparticles and inflammation in the lung.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; heme oxygenase-1; lung inflammation; platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecules-1; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

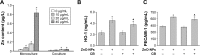



Similar articles
-
[The protein expression of heme oxygenase-1 and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecules-1 in human coronary artery endothelial cell induced by zinc oxide nanoparticle].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2015 Jan;33(1):11-4. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25876966 Chinese.
-
Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation and endocytosis were involved in zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced interleukin-8 overexpression in human bronchial epithelial cells.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2014 Apr;30(2):79-88. doi: 10.1007/s10565-014-9270-9. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24554449
-
[The role of heme oxygenase-1 on oxidative stress injury induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in human umbilical vein endothelial cells line EA.hy926 cells].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 6;52(11):1177-1181. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2018.11.016. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30419705 Chinese.
-
The toxicology of ion-shedding zinc oxide nanoparticles.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016;46(4):348-84. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1137864. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26963861 Review.
-
Beneficial and toxicological aspects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in animals.Vet Med Sci. 2022 Jul;8(4):1769-1779. doi: 10.1002/vms3.814. Epub 2022 May 19. Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35588498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Toxicokinetics, Tissue Distribution for Various Exposure Routes, Toxicological Effects, Toxicity Mechanism in Mammals, and an Approach for Toxicity Reduction.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Jan;202(1):9-23. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03644-w. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 36976450 Review.
-
Maternal engineered nanomaterial inhalation during gestation alters the fetal transcriptome.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018 Jan 10;15(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12989-017-0239-8. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29321036 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous Disruption of Beclin 1 Alleviates Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles-Induced Disturbance of Cholesterol Biosynthesis in Mouse Liver.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Dec 12;14:9865-9875. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S224179. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31849474 Free PMC article.
-
In light-sensitive drug delivery system nanoparticles mediate oxidative stress.Am J Transl Res. 2020 May 15;12(5):1469-1480. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32509156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered nanoparticle exposure and cardiovascular effects: the role of a neuronal-regulated pathway.Inhal Toxicol. 2018 Aug;30(9-10):335-342. doi: 10.1080/08958378.2018.1535634. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Inhal Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30604639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chupani L, Zuskova E, Niksirat H, et al. Effects of chronic dietary exposure of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the serum protein profile of juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Sci Total Environ. 2017;579:1504–1511. - PubMed
-
- Muhlfeld C, Gehr P, Rothen-Rutishauser B. Translocation and cellular entering mechanisms of nanoparticles in the respiratory tract. Swiss Med Wkly. 2008;138(27–28):387–391. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

