Optic perineuritis: a retrospective case series
- PMID: 28652823
- PMCID: PMC5476656
- DOI: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S125972
Optic perineuritis: a retrospective case series
Abstract
Optic perineuritis (OPN) is a rare inflammatory disorder involving the optic nerve sheath characterized by visual loss. OPN may be isolated and idiopathic or part of an underlying disorder. This case series aimed to help clinicians investigate and manage this disorder. Presentation, clinical findings, and treatment of OPN are discussed. After review of medical records at the ophthalmology clinic at Sahlgrenska University hospital in Gothenburg, Sweden, seven OPN patients (three men and four women) were identified and included in the present case series. These included idiopathic cases and patients with underlying disorders. Age at OPN diagnosis ranged from 26 to 64 years (mean age 55 years, median age 58 years). Five of the patients were treated with corticosteroids. This study suggests that a high-dose course of corticosteroids is important in the treatment of OPN in severely affected patients.
Keywords: corticosteroids; glucocorticoids; idiopathic; inflammation; magnetic resonance imaging; prednisone; vision.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
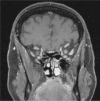

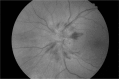
Similar articles
-
Optic perineuritis secondary to Wegener's granulomatosis.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Sep;37(7):712-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2009.02122.x. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19788669
-
Optic perineuritis: A Canadian case series and literature review.J Neurol Sci. 2021 Nov 15;430:120035. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.120035. Epub 2021 Oct 24. J Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34717266 Review.
-
Optic Perineuritis.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016 Feb;16(2):16. doi: 10.1007/s11910-015-0617-2. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26753870 Review.
-
Optic Perineuritis in Behçet Disease.J Neuroophthalmol. 2015 Dec;35(4):342-7. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000000264. J Neuroophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25996299
-
Optic perineuritis.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022 Nov 1;33(6):519-524. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000900. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36066374 Review.
Cited by
-
Caecocentral Scotoma: A Rare Presentation of Optic Perineuritis.Cureus. 2019 Nov 8;11(11):e6101. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6101. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31886042 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Optic Perineuritis in Tuberculosis-Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome.Cureus. 2022 Aug 2;14(8):e27600. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27600. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36059337 Free PMC article.
-
Optic Perineuritis Associated with Nivolumab Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2021 Jun 9;14(2):792-796. doi: 10.1159/000516275. eCollection 2021 May-Aug. Case Rep Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34248541 Free PMC article.
-
Optic Perineuritis and Its Association With Autoimmune Diseases.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 29;11:627077. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.627077. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33584521 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual presentation of neurosarcoidosis: Concurrent optic perineuritis and optic neuritis.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2021 Jan 25;11(1):104-107. doi: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_84_20. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33767965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennerdell JS, Dresner SC. The nonspecific orbital inflammatory syndromes. Surv Ophthalmol. 1984;29(2):93–103. - PubMed
-
- Purvin V, Kawasaki A, Jacobson DM. Optic perineuritis: clinical and radiographic features. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001;119(9):1299–1306. - PubMed
-
- Purvin V, Kawasaki A. Optic perineuritis secondary to Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;37(7):712–717. - PubMed
-
- Hickman SJ. Optic perineuritis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016;16(2):16. - PubMed
-
- Toshniwal P. Optic perineuritis with secondary syphilis. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1987;7(1):6–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

