Engineering CAR-T cells
- PMID: 28652918
- PMCID: PMC5482931
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-017-0102-y
Engineering CAR-T cells
Abstract
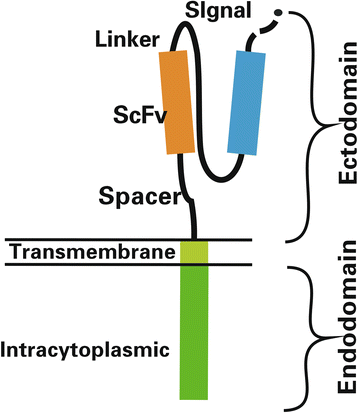
Chimeric antigen receptor redirected T cells (CAR-T cells) have achieved inspiring outcomes in patients with B cell malignancies, and are now being investigated in other hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. CAR-T cells are generated by the T cells from patients' or donors' blood. After the T cells are expanded and genetically modified, they are reinfused into the patients. However, many challenges still need to be resolved in order for this technology to gain widespread adoption. In this review, we first discuss the structure and evolution of chimeric antigen receptors. We then report on the tools used for production of CAR-T cells. Finally, we address the challenges posed by CAR-T cells.
Keywords: CAR-T cells; Chimeric antigen receptor redirected T cells; Evolution; Production; Structure; Viral vector.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

