Neural circuit of verbal humor comprehension in schizophrenia - an fMRI study
- PMID: 28652967
- PMCID: PMC5473647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.06.005
Neural circuit of verbal humor comprehension in schizophrenia - an fMRI study
Abstract
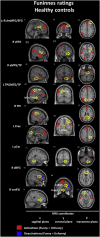
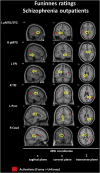
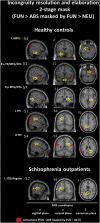
Individuals with schizophrenia exhibit problems with understanding the figurative meaning of language. This study evaluates neural correlates of diminished humor comprehension observed in schizophrenia. The study included chronic schizophrenia (SCH) outpatients (n = 20), and sex, age and education level matched healthy controls (n = 20). The fMRI punchline based humor comprehension task consisted of 60 stories of which 20 had funny, 20 nonsensical and 20 neutral (not funny) punchlines. After the punchlines were presented, the participants were asked to indicate whether the story was comprehensible and how funny it was. Three contrasts were analyzed in both groups reflecting stages of humor processing: abstract vs neutral stories - incongruity detection; funny vs abstract - incongruity resolution and elaboration; and funny vs neutral - complete humor processing. Additionally, parametric modulation analysis was performed using both subjective ratings separately. Between-group comparisons revealed that the SCH subjects had attenuated activation in the right posterior superior temporal gyrus (BA 41) in case of irresolvable incongruity processing of nonsensical puns; in the left dorsomedial middle and superior frontal gyri (BA 8/9) in case of incongruity resolution and elaboration processing of funny puns; and in the interhemispheric dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (BA 24) in case of complete processing of funny puns. Additionally, during comprehensibility ratings the SCH group showed a suppressed activity in the left dorsomedial middle and superior frontal gyri (BA 8/9) and revealed weaker activation during funniness ratings in the left dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (BA 24). Interestingly, these differences in the SCH group were accompanied behaviorally by a protraction of time in both types of rating responses and by indicating funny punchlines less comprehensible. Summarizing, our results indicate neural substrates of humor comprehension processing impairments in schizophrenia, which is accompanied by fronto-temporal hypoactivation.
Keywords: ABS, absurd/nonsensical punchline; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; BA, Brodmann's area; CON, healthy controls/control group; Communication skills; EEG, electroencephalography; ERPs, EEG event-related potentials; FDR, False Discovery Rate; FUN, funny punchline; FWHM, full-width-at-half-maximum; Figurative meaning; Functional magnetic resonance imaging; GLM, general linear model; Humor; IFG, inferior frontal gyrus; IPL, Inferior Parietal Lobule; ISI, interstimulus-interval; L, left hemisphere; MFG, medial frontal gyrus; MNI, Montreal Neurological Institute coordinates; MOG, middle occipital gyrus; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MTG, middle temporal gyrus; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; NEU, neutral/unfunny punchline; PANSS, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PFC, prefrontal cortex; R, right hemisphere; RHLB, Right Hemisphere Language Battery; RT, reaction time; SCH, schizophrenia outpatients/clinical group; SD, standard deviations; SEM, standard error of the mean; SFG, Superior Frontal Gyrus; SOA, stimulus onset asynchrony; STG, superior temporal gyrus; Schizophrenia; TP, temporal pole; TPJ, temporoparietal junction; ToM, theory of mind.; dACC, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; dlPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; dmMFG, dorsomedial Middle Frontal Gyrus; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; fNIRS, functional near-infrared spectroscopy; k, number of voxels in analyzed cluster size; ns, non-significant group difference; pSTG, posterior Superior Temporal Gyrus; sLORETA, standardized low resolution brain electromagnetic tomography analysis.
Figures

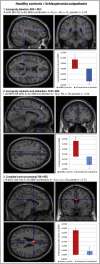
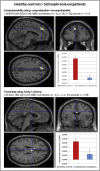

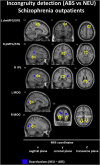

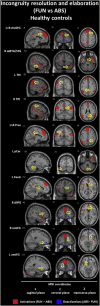




References
-
- Adamczyk P., Daren A., Sułecka A., Błądziński P., Cichocki Ł., Kalisz A., Gawęda Ł., Cechnicki A. Do better communication skills promote sheltered employment in schizophrenia? Schizophr. Res. 2016;176:331–339. - PubMed
-
- Atkins M., Burgess A., Bottomley C., Riccio M. Chlorpromazine equivalents: a consensus of opinion for both clinical and research applications. Psychiatr. Bull. 1997;21:224–226.
-
- Bartolo A., Benuzzi F., Nocetti L., Baraldi P., Nichelli P. Humor comprehension and appreciation: an FMRI study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2006;18:1789–1798. - PubMed
-
- Benton E., Bryan K. Right cerebral hemisphere damage: incidence of language problems. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. Int. Z. Rehabil. Rev. Int. Rech. Readaptation. 1996;19:47–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

