Proteomics data on MAP Kinase Kinase 3 knock out bone marrow derived macrophages exposed to cigarette smoke extract
- PMID: 28653025
- PMCID: PMC5476452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.05.049
Proteomics data on MAP Kinase Kinase 3 knock out bone marrow derived macrophages exposed to cigarette smoke extract
Abstract
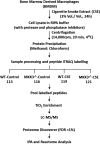
This data article reports changes in the phosphoproteome and total proteome of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) exposed WT and MAP Kinase Kinase 3 knock out (MKK3-/-) bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM). The dataset generated is helpful for understanding the mechanism of CSE induced inflammation and the role of MAP kinase signaling pathway. The cellular proteins were labeled with isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ®) reagents and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The standard workflow module for iTRAQ® quantification within the Proteome Discoverer was utilized for the data analysis. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software and Reactome was used to identify enriched canonical pathways and molecular networks (Mannam et al., 2016) [1]. All the associated mass spectrometry data has been deposited in the Yale Protein Expression Database (YPED) with the web-link to the data: http://yped.med.yale.edu/repository/ViewSeriesMenu.do;jsessionid=6A5CB07543D8B529FAE8C3FCFE29471D?series_id=5044&series_name=MMK3+Deletion+in+MEFs.
Keywords: Cigarette smoke; Inflammation; MKK3; Proteomics; iTRAQ®.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SILAC based protein profiling data of MKK3 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Data Brief. 2016 Mar 2;7:418-22. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.02.034. eCollection 2016 Jun. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 26977448 Free PMC article.
-
MKK3 influences mitophagy and is involved in cigarette smoke-induced inflammation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27717867
-
Quantitative proteomics analysis using 2D-PAGE to investigate the effects of cigarette smoke and aerosol of a prototypic modified risk tobacco product on the lung proteome in C57BL/6 mice.J Proteomics. 2016 Aug 11;145:237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.05.037. Epub 2016 Jun 5. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27268958
-
Shotgun proteomics using the iTRAQ isobaric tags.Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2006 Jun;5(2):112-20. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ell018. Epub 2006 May 10. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2006. PMID: 16772272 Review.
-
Standardization approaches in absolute quantitative proteomics with mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018 Nov;37(6):715-737. doi: 10.1002/mas.21542. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018. PMID: 28758227 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics comparisons of p-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) resistance in folC mutated and un-mutated Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):248-261. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1568179. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 30866779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mannam P., Rauniyar N., Lam T.T., Luo R., Lee P.J., Srivastava A. MKK3 influences mitophagy and is involved in cigarette smoke-induced inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016;101:102–115. - PubMed
-
- Pelech S.L., Charest D.L. MAP kinase-dependent pathways in cell cycle control. Progress. Cell Cycle Res. 1995;1:33–52. - PubMed
-
- Rossa C., Ehmann K., Liu M., Patil C., Kirkwood K.L. MKK3/6-p38 MAPK signaling is required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced RANKL expression in bone marrow stromal cells. J. Interferon Cytokine Res.: Off. J. Int. Soc. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006;26:719–729. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous