Assembly and Tracking of Microbial Community Development within a Microwell Array Platform
- PMID: 28654053
- PMCID: PMC5608264
- DOI: 10.3791/55701
Assembly and Tracking of Microbial Community Development within a Microwell Array Platform
Abstract
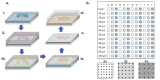
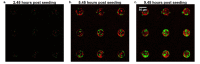
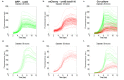
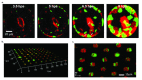
The development of microbial communities depends on a combination of complex deterministic and stochastic factors that can dramatically alter the spatial distribution and activities of community members. We have developed a microwell array platform that can be used to rapidly assemble and track thousands of bacterial communities in parallel. This protocol highlights the utility of the platform and describes its use for optically monitoring the development of simple, two-member communities within an ensemble of arrays within the platform. This demonstration uses two mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, part of a series of mutants developed to study Type VI secretion pathogenicity. Chromosomal inserts of either mCherry or GFP genes facilitate the constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins with distinct emission wavelengths that can be used to monitor community member abundance and location within each microwell. This protocol describes a detailed method for assembling mixtures of bacteria into the wells of the array and using time-lapse fluorescence imaging and quantitative image analysis to measure the relative growth of each member population over time. The seeding and assembly of the microwell platform, the imaging procedures necessary for the quantitative analysis of microbial communities within the array, and the methods that can be used to reveal interactions between microbial species area all discussed.
References
-
- Nunan N, Wu K, Young IM, Crawford JW, Ritz K. Spatial distribution of bacterial communities and their relationships with the micro-architecture of soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2003;44:203–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources