The development of anticancer ruthenium(ii) complexes: from single molecule compounds to nanomaterials
- PMID: 28654103
- PMCID: PMC5624840
- DOI: 10.1039/c7cs00195a
The development of anticancer ruthenium(ii) complexes: from single molecule compounds to nanomaterials
Abstract
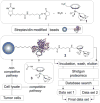
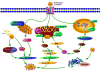
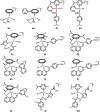
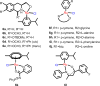
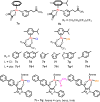
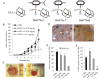
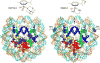
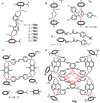
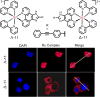
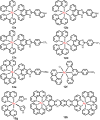
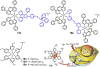
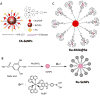
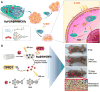
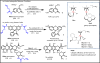
Cancer is rapidly becoming the top killer in the world. Most of the FDA approved anticancer drugs are organic molecules, while metallodrugs are very scarce. The advent of the first metal based therapeutic agent, cisplatin, launched a new era in the application of transition metal complexes for therapeutic design. Due to their unique and versatile biochemical properties, ruthenium-based compounds have emerged as promising anti-cancer agents that serve as alternatives to cisplatin and its derivertives. Ruthenium(iii) complexes have successfully been used in clinical research and their mechanisms of anticancer action have been reported in large volumes over the past few decades. Ruthenium(ii) complexes have also attracted significant attention as anticancer candidates; however, only a few of them have been reported comprehensively. In this review, we discuss the development of ruthenium(ii) complexes as anticancer candidates and biocatalysts, including arene ruthenium complexes, polypyridyl ruthenium complexes, and ruthenium nanomaterial complexes. This review focuses on the likely mechanisms of action of ruthenium(ii)-based anticancer drugs and the relationship between their chemical structures and biological properties. This review also highlights the catalytic activity and the photoinduced activation of ruthenium(ii) complexes, their targeted delivery, and their activity in nanomaterial systems.
Figures


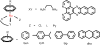
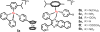
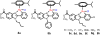
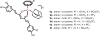






Similar articles
-
Monomeric and dimeric coordinatively saturated and substitutionally inert Ru(ii) polypyridyl complexes as anticancer drug candidates.Chem Soc Rev. 2017 Nov 27;46(23):7317-7337. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00356k. Chem Soc Rev. 2017. PMID: 29027562 Review.
-
DNA binding mode of ruthenium complexes and relationship to tumor cell toxicity.Drug Resist Updat. 2006 Jun;9(3):111-22. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2006.05.002. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Drug Resist Updat. 2006. PMID: 16790363 Review.
-
Vanadium, Ruthenium and Copper Compounds: A New Class of Nonplatinum Metallodrugs with Anticancer Activity.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(2):112-148. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160824162546. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27554807 Review.
-
Functionalization and cancer-targeting design of ruthenium complexes for precise cancer therapy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2019 Aug 15;55(67):9904-9914. doi: 10.1039/c9cc04098f. Chem Commun (Camb). 2019. PMID: 31360938 Review.
-
Recent advances in ruthenium (III) complex-loaded nanomaterial for enhanced cancer therapy efficacy.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025 Mar;51(3):169-179. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2025.2455428. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39836522 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the factors controlling the photo-oxidation of natural DNA by enantiomerically pure intercalating ruthenium polypyridyl complexes through TA/TRIR studies with polydeoxynucleotides and mixed sequence oligodeoxynucleotides.Chem Sci. 2020 Aug 6;11(32):8600-8609. doi: 10.1039/d0sc02413a. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34123120 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual enantioselective cytoplasm-to-nucleus translocation and photosensitization of the chiral Ru(II) cationic complex via simple ion-pairing with lipophilic weak acid counter-anions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 24;51(7):3041-3054. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad155. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36938880 Free PMC article.
-
Ratiometric Luminescent Nanoprobes Based on Ruthenium and Terbium-Containing Metallopolymers for Intracellular Oxygen Sensing.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Aug 2;11(8):1290. doi: 10.3390/polym11081290. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31382391 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Activity of Half-Sandwich Ru, Rh and Ir Complexes with Chrysin Derived Ligands: Strong Effect of the Side Chain in the Ligand and Influence of the Metal.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 23;13(10):1540. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101540. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34683834 Free PMC article.
-
Rationally designed Ru(ii)-metallacycle chemo-phototheranostic that emits beyond 1000 nm.Chem Sci. 2022 May 18;13(22):6541-6549. doi: 10.1039/d2sc01518h. eCollection 2022 Jun 7. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35756528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi G, Monro S, Hennigar R, Colpitts J, Fong J, Kasimova K, Yin H, DeCoste R, Spencer C, Chamberlain L. Coord Chem Rev. 2015;282:127–138.
-
- Garbutcheon-Singh KB, Grant MP, Harper BW, Krause-Heuer AM, Manohar M, Orkey N, Aldrich-Wright JR. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11:521–542. - PubMed
-
- Tao Y, Li M, Ren J, Qu X. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:8636–8663. - PubMed
-
- Li F, Collins JG, Keene FR. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:2529–2542. - PubMed
-
- Muhammad N, Guo Z. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014;19:144–153. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

