EcoBLMcrX, a classical modification-dependent restriction enzyme in Escherichia coli B: Characterization in vivo and in vitro with a new approach to cleavage site determination
- PMID: 28654677
- PMCID: PMC5487053
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179853
EcoBLMcrX, a classical modification-dependent restriction enzyme in Escherichia coli B: Characterization in vivo and in vitro with a new approach to cleavage site determination
Abstract
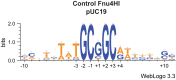
Here we characterize the modification-dependent restriction enzyme (MDE) EcoBLMcrX in vivo, in vitro and in its genomic environment. MDE cleavage of modified DNAs protects prokaryote populations from lethal infection by bacteriophage with highly modified DNA, and also stabilizes lineages by reducing gene import when sparse modification occurs in the wrong context. The function and distribution of MDE families are thus important. Here we describe the properties of EcoBLMcrX, an enzyme of the E. coli B lineage, in vivo and in vitro. Restriction in vivo and the genome location of its gene, ecoBLmcrX, were determined during construction and sequencing of a B/K-12 hybrid, ER2566. In classical restriction literature, this B system was named r6 or rglAB. Like many genome defense functions, ecoBLmcrX is found within a genomic island, where gene content is variable among natural E. coli isolates. In vitro, EcoBLMcrX was compared with two related enzymes, BceYI and NhoI. All three degrade fully cytosine-modified phage DNA, as expected for EcoBLMcrX from classical T4 genetic data. A new method of characterizing MDE specificity was developed to better understand action on fully-modified targets such as the phage that provide major evolutionary pressure for MDE maintenance. These enzymes also cleave plasmids with m5C in particular motifs, consistent with a role in lineage-stabilization. The recognition sites were characterized using a site-ranking approach that allows visualization of preferred cleavage sites when fully-modified substrates are digested. A technical constraint on the method is that ligation of one-nucleotide 5' extensions favors G:C over A:T approximately five-fold. Taking this bias into account, we conclude that EcoBLMcrX can cleave 3' to the modified base in the motif Rm5C|. This is compatible with, but less specific than, the site reported by others. Highly-modified site contexts, such as those found in base-substituted virulent phages, are strongly preferred.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Iurlaro M, McInroy GR, Burgess HE, Dean W, Raiber EA, Bachman M, et al. In vivo genome-wide profiling reveals a tissue-specific role for 5-formylcytosine. Genome Biol. 2016;17(1):141 doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1001-5 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4928330. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun Z, Dai N, Borgaro JG, Quimby A, Sun D, Correa IR Jr., et al. A sensitive approach to map genome-wide 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-formylcytosine at single-base resolution. Mol Cell. 2015;57(4):750–61. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.035 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stucken K, Koch R, Dagan T. Cyanobacterial defense mechanisms against foreign DNA transfer and their impact on genetic engineering. Biol Res. 2013;46(4):373–82. doi: 10.4067/S0716-97602013000400009 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Monk IR, Shah IM, Xu M, Tan MW, Foster TJ. Transforming the untransformable: application of direct transformation to manipulate genetically Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. MBio. 2012;3(2):e00277-11-e-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00277-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3312211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu SY, Corvaglia AR, Chan SH, Zheng Y, Linder P. A type IV modification-dependent restriction enzyme SauUSI from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(13):5597–610. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr098 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3141236. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

