[Prognostic value of the revised international staging system for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients]
- PMID: 28655089
- PMCID: PMC7342976
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2017.06.003
[Prognostic value of the revised international staging system for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients]
Abstract
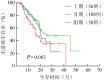
Objective: To assess the prognostic value of revised international staging system (R-ISS) for multiple myeloma (MM) in real world. Methods: A total of 202 newly diagnosis symptomatic MM patients were enrolled from May 2010 to April 2015 and the clinical data were retrospectively analyzed. All the patients received at least four courses of bortezomib-based or thalidomide-based induction therapy. Results: With a median follow-up of 31 months, the cohort included 56 cases in R-ISSⅠ, 108 in R-ISS Ⅱ, and 38 in R-ISS Ⅲ, and the median OS was not reached/61/38 months, respectively (P=0.001). According to the ISS system, 62 patients were classified in ISS-Ⅰ, 70 in ISS-Ⅱ and 70 in ISS-Ⅲ, with the median OS was 58, 52 and 40 months, respectively (P=0.001). The relative risk (HR) of R-ISS stage Ⅲ vs Ⅰ, Ⅱ vs Ⅰ were 9.606 (P=0.008) and 4.038 (P=0.029). The HR of Ⅲ vs Ⅰ, Ⅱ vs Ⅰ of ISS system were 4.127 (P=0.070) and 2.877 (P=0.005). In the subgroup analysis, R-ISS predicted survival for patients who were not transplanted (P=0.003) , receiving bortezomib-based therapy (P=0.010) , and patients younger than 65 years (P=0.001). Conclusion: R-ISS system could better predict prognosis for OS in unselected nonclinical trial myeloma patients than ISS system, especially for the younger patients, patients with bortezomib-based therapy, and patients without transplantation.
目的: 探讨修订的国际分期系统(R-ISS)在真实世界中对初诊多发性骨髓瘤(MM)患者的适用性。 方法: 回顾性分析2010年5月至2015年4月新诊断的202例MM患者的临床资料。所有患者均接受基于硼替佐米或沙利度胺为主的方案诱导治疗至少4个疗程。以国际分期系统(ISS)为对照,分析R-ISS的预后意义。 结果: 202例患者中,男124例,女78例,中位年龄57(28~81)岁。中位随访31个月,采用R-ISS分期,Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ期患者分别为56、108、38例,中位总体生存(OS)时间分别为未达到、61个月和38个月,三期间差异有统计学意义(P=0.001);采用ISS分期,Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ期患者分别为62、70、70例,中位OS时间分别为58、52和40个月,三期间差异有统计学意义(P=0.001)。采用Cox预后风险模式分析发现:R-ISS预后Ⅲ对Ⅰ、Ⅱ对Ⅰ期的HR值分别为9.606和4.038,P值分别为0.008和0.029;ISS预后的HR值分别为4.127和2.877,P值分别为0.070和0.005。亚组分析结果显示,未行移植(P=0.003)、接受硼替佐米为主的方案治疗(P=0.010)及年龄小于65岁(P=0.001)R-ISS不同分期患者的OS时间差异均有统计学意义。 结论: R-ISS能更好地区分初诊MM患者的OS时间,尤其对于接受硼替佐米治疗为主、年轻、未行移植患者的预后评估价值较为突出,对中国MM患者具有重要的预后价值。.
Keywords: Multiple myeloma; Prognosis; R-ISS system.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous