Angiomotin Family Members: Oncogenes or Tumor Suppressors?
- PMID: 28656002
- PMCID: PMC5485632
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.19603
Angiomotin Family Members: Oncogenes or Tumor Suppressors?
Abstract
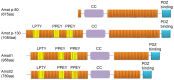
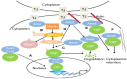
Angiomotin (Amot) family contains three members: Amot (p80 and p130 isoforms), Amot-like protein 1 (Amotl1), and Amot-like protein 2 (Amotl2). Amot proteins play an important role in tube formation and migration of endothelial cells and the regulation of tight junctions, polarity, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in epithelial cells. Moreover, these proteins regulate the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. In most cancers, Amot family members promote the proliferation and invasion of cancer cells, including breast cancer, osteosarcoma, colon cancer, prostate cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, liver cancer, and renal cell cancer. However, in glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, and lung cancer, Amot inhibits the growth of cancer cells. In addition, there are controversies on the regulation of Yes-associated protein (YAP) by Amot. Amot promotes either the internalization of YAP into the nucleus or the retention of YAP in the cytoplasm of different cell types. Moreover, Amot regulates the AMPK, mTOR, Wnt, and MAPK signaling pathways. However, it is unclear whether Amot is an oncogene or a tumor suppressor gene in different cellular processes. This review focuses on the multifunctional roles of Amot in cancers.
Keywords: Angiomotin; YAP.; cancer; oncogene; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The p130 isoform of angiomotin is required for Yap-mediated hepatic epithelial cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.Sci Signal. 2013 Sep 3;6(291):ra77. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004060. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24003254 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo pathway-independent restriction of TAZ and YAP by angiomotin.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 4;286(9):7018-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C110.212621. Epub 2011 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21224387 Free PMC article.
-
Angiomotin promotes the malignant potential of colon cancer cells by activating the YAP-ERK/PI3K-AKT signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2016 Dec;36(6):3619-3626. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5194. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27779692
-
Angiomotin'g YAP into the nucleus for cell proliferation and cancer development.Sci Signal. 2013 Sep 3;6(291):pe27. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004573. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24003252 Review.
-
The role of Motin family proteins in tumorigenesis-an update.Oncogene. 2023 Apr;42(16):1265-1271. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02677-8. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36973516 Review.
Cited by
-
O-GlcNAcylation: An Emerging Protein Modification Regulating the Hippo Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;14(12):3013. doi: 10.3390/cancers14123013. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IQGAP1, AmotL2, and FKBP51 Scaffoldins in the Glioblastoma Microenvironment.J Histochem Cytochem. 2019 Jul;67(7):481-494. doi: 10.1369/0022155419833334. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Histochem Cytochem. 2019. PMID: 30794467 Free PMC article.
-
AMOTL2‑knockdown promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma by regulating β‑catenin nuclear localization.Oncol Rep. 2021 Jul;46(1):139. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8090. Epub 2021 May 26. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34036399 Free PMC article.
-
Angiomotin regulates budding and spread of Ebola virus.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 19;295(25):8596-8601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC120.013171. Epub 2020 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32381509 Free PMC article.
-
Bothrops Jararaca Snake Venom Modulates Key Cancer-Related Proteins in Breast Tumor Cell Lines.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 25;13(8):519. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080519. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bratt A, Wilson WJ, Troyanovsky B, Aase K, Kessler R, Van Meir EG. et al. Angiomotin belongs to a novel protein family with conserved coiled-coil and PDZ binding domains. Gene. 2002;298:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996;86:353–364. - PubMed
-
- O'Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal RA, Cao Y. et al. Angiostatin: a circulating endothelial cell inhibitor that suppresses angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology. 1994;59:471–482. - PubMed
-
- Ji WR, Castellino FJ, Chang Y, Deford ME, Gray H, Villarreal X. et al. Characterization of kringle domains of angiostatin as antagonists of endothelial cell migration, an important process in angiogenesis. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 1998;12:1731–1738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

