Effect of Huayu Tongluo Herbs on Reduction of Proteinuria via Inhibition of Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 28656052
- PMCID: PMC5471573
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3054145
Effect of Huayu Tongluo Herbs on Reduction of Proteinuria via Inhibition of Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
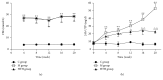
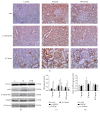
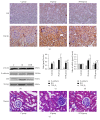
The study investigated the expression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in diabetic rats and the intervention effect of Huayu Tongluo herbs (HTH). Ten rats were randomly selected as control group and the remaining rats were established as diabetic models. The diabetic rats were randomly divided into model group and HTH treatment group. The intervention was intragastric administration in all rats for 20 weeks. At the end of every 4 weeks, fasting blood glucose and 24 h urinary total protein quantitatively were measured. At the end of the 20th week, biochemical parameters and body weight were tested. The kidney tissues were observed under light microscope and transmission electron microscopy. We examined Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway key proteins and renal interstitial fibrosis related molecular markers expression. The results showed that HTH could reduce urinary protein excretion and relieve renal pathological damage. Wnt4, p-GSK3β (S9), and β-catenin expression were decreased in the signaling pathway, but GSK3β level was not changed by HTH in diabetic rats. Furthermore, the expressions of TGF-β1 and ILK were decreased, but the level of E-cadherin was increased in diabetic rats after treatment with HTH. This study demonstrated that HTH could inhibit the high expression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in kidney of diabetic rats. The effect might be one of the main ways to reduce urinary protein excretion.
Figures

References
-
- Long X. J., Lin S., Zhang X., et al. Correlation between podocyte excretion and proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy patients. Journal of Medical Colleges of PLA. 2010;25(3):180–186. doi: 10.1016/S1000-1948(10)60037-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

