Determination of Epimedin B in Rat Plasma and Tissue by LC-MS/MS: Application in Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution Studies
- PMID: 28656123
- PMCID: PMC5471579
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7194075
Determination of Epimedin B in Rat Plasma and Tissue by LC-MS/MS: Application in Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution Studies
Abstract
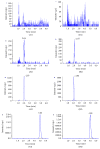
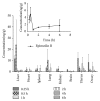
A simple, sensitive, and specific liquid chromatography tandem mass-spectrometric method was developed and validated for the determination of epimedin B in rat plasma and tissue samples. After being processed with a protein precipitation method, these samples were separated on an Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18 column with an isocratic mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (32 : 68, v/v). The calibration curve of epimedin B was linear over the concentration range from 1 to 500 ng/mL in plasma and tissue homogenate. The method was then applied to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution studies after a single oral administration of Herba Epimedii extract to SD rats. Results showed that epimedin B reached the plasma peak concentration at 0.4 h and the terminal elimination half-life was 1.6 h in rat plasma, and the plasma area under the curve from time zero to infinity (AUC0-∞ ) was 14.35 μg/L·h. The concentration distribution of epimedin B in rat tissue was in the following order: liver > ovary > womb > lung > kidney > spleen > heart > brain, indicating that the compound could be widely distributed in rat, and the reproductive system may be the principal target of epimedin B for female rat.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of epimedin C after oral administration of epimedin C and Herba Epimedii extract in rats.Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 May;28(5):630-6. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3081. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014. PMID: 24264996
-
Determination of epimedin C in rat plasma by reversed-phase high-performance chromatography after oral administration of Herba Epimedii extract.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005 Jul 25;821(2):235-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.04.012. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15935743
-
Plasma pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of cajaninstilbene acid in rats by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010 Jun 5;52(2):273-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Jan 15. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010. PMID: 20116956
-
Determination of cefadroxil in rat plasma and urine using LC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetic and urinary excretion studies.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Feb 1;947-948:103-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.12.027. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24412692
-
Simultaneous determination of timosaponin B-II and A-III in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetic study.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Aug 15;965:119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.06.017. Epub 2014 Jun 21. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25016164
References
-
- Liu R.-H., Kang X., Xu L.-P., et al. Effects of the combined extracts of Herba Epimedii and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi on bone mineral content and bone turnover in osteoporotic rats. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2015;15(1, article 112) doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0641-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan B. C. L., Lee H. Y., Siu W. S., et al. Suppression of mast cell activity contributes to the osteoprotective effect of an herbal formula containing Herba Epimedii, Fructus Ligustri Lucidi and Fructus Psoraleae. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2014;66(3):437–444. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12166. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Niu R. Action of the drug Herba Epimedii on testosterone of the mouse plasma and its accessory sexual organ before and after processing. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 1989;14(9):530–574. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

