Efficacy and Safety of Cerebrolysin for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 28656143
- PMCID: PMC5474547
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4191670
Efficacy and Safety of Cerebrolysin for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
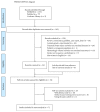
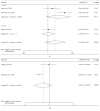
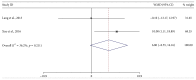
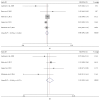
Cerebrolysin was reported to be effective in the neurological improvement of patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in experimental models, while data from clinical trials were inconsistent. We performed a meta-analysis to explore the efficacy and safety of cerebrolysin for AIS. PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library were searched for randomized controlled trials, which intervened within 72 hours after the stroke onset. We investigated the efficacy and safety outcomes, respectively. Risk ratios and mean differences were pooled with fixed-effects model or random-effects model. Seven studies were identified, involving 1779 patients with AIS. The summary results failed to demonstrate significant superiority of cerebrolysin in the assessment of efficacy outcomes of mRS and BI. Similarly, administration of cerebrolysin had neutral effects on safety outcomes compared with placebo, including mortality and SAE. However, the number of included studies was small, especially in the analysis of efficacy outcomes, which might cause publication bias and inaccurate between-studies variance in the meta-analysis. Conclusively, although it seemed to be safe, routine use of cerebrolysin to improve the long-term rehabilitation after stroke could not be supported by available evidence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in early post-stroke recovery: a meta-analysis of nine randomized clinical trials.Neurol Sci. 2018 Apr;39(4):629-640. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3214-0. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29248999 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin treatment in early recovery after acute ischemic stroke: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter clinical trial.J Med Life. 2017 Jul-Sep;10(3):153-160. J Med Life. 2017. PMID: 29075343 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in motor function recovery after stroke: a meta-analysis of the CARS trials.Neurol Sci. 2017 Oct;38(10):1761-1769. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3037-z. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28707130 Free PMC article.
-
Safety profile of Cerebrolysin: clinical experience from dementia and stroke trials.Drugs Today (Barc). 2012 Apr;48 Suppl A:63-9. doi: 10.1358/dot.2012.48(Suppl.A).1739724. Drugs Today (Barc). 2012. PMID: 22514795 Review.
-
Cerebrolysin: a multi-target drug for recovery after stroke.Expert Rev Neurother. 2018 Aug;18(8):681-687. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2018.1500459. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018. PMID: 30004268 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous defense mechanism-based neuroprotection in large-vessel acute ischemic stroke: A hope for future.Brain Circ. 2024 Mar 21;10(1):51-59. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_56_23. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. Brain Circ. 2024. PMID: 38655439 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in early post-stroke recovery: a meta-analysis of nine randomized clinical trials.Neurol Sci. 2018 Apr;39(4):629-640. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3214-0. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29248999 Free PMC article.
-
Extended Poststroke Rehabilitation Combined with Cerebrolysin Promotes Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Early Subacute Phase of Rehabilitation: A Randomized Clinical Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Feb 3;59(2):291. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020291. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837492 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Cerebrolysin in combination with high-dose aspirin antithrombotic treatment of ischemic stroke: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Sep 24;9(9):e04863. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4863. eCollection 2021 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34594556 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Neuroprotective Strategies in Enhancing Post-stroke Recovery: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses and Clinical Trials.Cureus. 2024 Oct 12;16(10):e71343. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71343. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39534815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murray C. J., Vos T., Lozano R., Naghavi M., Flaxman A. D., Michaud C., et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

