Sulfide Homeostasis and Nitroxyl Intersect via Formation of Reactive Sulfur Species in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 28656172
- PMCID: PMC5480029
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00082-17
Sulfide Homeostasis and Nitroxyl Intersect via Formation of Reactive Sulfur Species in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
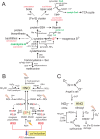
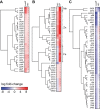
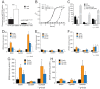
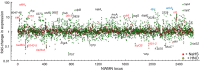
Staphylococcus aureus is a commensal human pathogen and a major cause of nosocomial infections. As gaseous signaling molecules, endogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO·) protect S. aureus from antibiotic stress synergistically, which we propose involves the intermediacy of nitroxyl (HNO). Here, we examine the effect of exogenous sulfide and HNO on the transcriptome and the formation of low-molecular-weight (LMW) thiol persulfides of bacillithiol, cysteine, and coenzyme A as representative of reactive sulfur species (RSS) in wild-type and ΔcstR strains of S. aureus. CstR is a per- and polysulfide sensor that controls the expression of a sulfide oxidation and detoxification system. As anticipated, exogenous sulfide induces the cst operon but also indirectly represses much of the CymR regulon which controls cysteine metabolism. A zinc limitation response is also observed, linking sulfide homeostasis to zinc bioavailability. Cellular RSS levels impact the expression of a number of virulence factors, including the exotoxins, particularly apparent in the ΔcstR strain. HNO, like sulfide, induces the cst operon as well as other genes regulated by exogenous sulfide, a finding that is traced to a direct reaction of CstR with HNO and to an endogenous perturbation in cellular RSS, possibly originating from disassembly of Fe-S clusters. More broadly, HNO induces a transcriptomic response to Fe overload, Cu toxicity, and reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species and shares similarity with the sigB regulon. This work reveals an H2S/NO· interplay in S. aureus that impacts transition metal homeostasis and virulence gene expression. IMPORTANCE Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a toxic molecule and a recently described gasotransmitter in vertebrates whose function in bacteria is not well understood. In this work, we describe the transcriptomic response of the major human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus to quantified changes in levels of cellular organic reactive sulfur species, which are effector molecules involved in H2S signaling. We show that nitroxyl (HNO), a recently described signaling intermediate proposed to originate from the interplay of H2S and nitric oxide, also induces changes in cellular sulfur speciation and transition metal homeostasis, thus linking sulfide homeostasis to an adaptive response to antimicrobial reactive nitrogen species.
Keywords: hydrogen sulfide; nitric oxide; nitroxyl; persulfide; reactive nitrogen species; reactive sulfur species; transcriptomics.
Figures



References
-
- Soutourina O, Poupel O, Coppée JY, Danchin A, Msadek T, Martin-Verstraete I. 2009. CymR, the master regulator of cysteine metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus, controls host sulphur source utilization and plays a role in biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol 73:194–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06760.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanous C, Soutourina O, Raynal B, Hullo MF, Mervelet P, Gilles AM, Noirot P, Danchin A, England P, Martin-Verstraete I. 2008. The CymR regulator in complex with the enzyme CysK controls cysteine metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 283:35551–35560. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805951200. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
