Hydrogen sulfide reduced renal tissue fibrosis by regulating autophagy in diabetic rats
- PMID: 28656209
- PMCID: PMC5561787
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6813
Hydrogen sulfide reduced renal tissue fibrosis by regulating autophagy in diabetic rats
Abstract
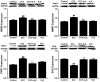
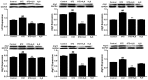
The present study aimed to explore the effect of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on renal tissue fibrosis and its mechanism in diabetic rats. Rats were randomly divided into four groups (n=13/group): Control group; induced diabetes mellitus group (STZ); induced diabetes mellitus treated with H2S group (STZ + H2S); normal rats treated with H2S group (H2S). The diabetic model was induced by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of 40 mg/kg body weight streptozotocin (STZ); the control group was treated with saline every day (i.p); NaHS (100 µmol/kg i.p.) was administered to rats of STZ + H2S group and H2S group. After 8 weeks, rat body weight and 24 h proteinuria levels were determined in each group, renal pathological morphology was analyzed by Masson's trichrome staining, collagen IV content was detected by immunohistochemistry, and periodic acid‑Schiff (PAS) staining was performed on renal glomerular and tubular basement membranes. The expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), MMP7, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1), superoxide dismutase (SOD), serine/threonine kinase AKT, transforming growth factor (TGF)‑β1, nuclear factor (NF)‑κB and several autophagy related proteins were assessed by western blot analysis. Compared with the control group, renal tissue fibrosis was observed, collagen IV expression and the 24 h proteinuria quantity was markedly increased and the amount of PAS positive material in renal glomerular and tubular basement membranes was notably increased in STZ‑treated rats. Furthermore, the expression levels of MMP9, MMP7, TIMP1, autophagy‑associated proteins, AKT, TGF‑β1 and NF‑κB protein were significantly increased, and SOD expression levels were significantly decreased in the STZ group compared with the control (P<0.05). In the H2S+STZ group, renal tissue fibrosis and the expression of collagen IV were improved, 24 h proteinuria was decreased, the amount of PAS positive material in renal glomerular and tubular basement membranes was decreased, the expression levels MMP9, MMP7, TIMP1, autophagy‑associated proteins, AKT, TGF‑β1 and NF‑κB protein were significantly decreased, and the expression levels of SOD were significantly increased compared with the STZ group (P<0.05). In conclusion, H2S may improve renal tissue fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy, upregulating SOD and downregulating AKT, TGF‑β1 and NF-κB.
Figures




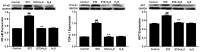
References
-
- Velentzas PD, Velentzas AD, Mpakou VE, Antonelou MH, Margaritis LH, Papassideri IS, Stravopodis DJ. Detrimental effects of proteasome inhibition activity in Drosophila melanogaster: Implication of ER stress, autophagy, and apoptosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2013;29:13–37. doi: 10.1007/s10565-012-9235-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

