Acute renal failure, severe sodium and potassium imbalance and sudden tetraplegia
- PMID: 28657059
- PMCID: PMC5477952
- DOI: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfq017
Acute renal failure, severe sodium and potassium imbalance and sudden tetraplegia
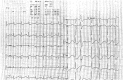
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disorders of body fluids, sodium and potassium in chronic renal failure.Am J Med. 1982 Mar;72(3):536-50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90523-x. Am J Med. 1982. PMID: 7036741 Review.
-
Body water and electrolyte composition in acute renal failure.Can Med Assoc J. 1971 Jun 5;104(11):1000-3. Can Med Assoc J. 1971. PMID: 5576038 Free PMC article.
-
[Secondary hyperkalaemic acute flaccid tetraplegia].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2009 Apr;28(4):381-3. doi: 10.1016/j.annfar.2009.02.014. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2009. PMID: 19304442 French.
-
Inner medullary collecting duct function in ischemic acute renal failure.Clin Invest Med. 1988 Jun;11(3):157-66. Clin Invest Med. 1988. PMID: 3402104
-
What is the optimal serum potassium level in cardiovascular patients?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Jan 21;43(2):155-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.06.021. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 14736430 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical and Fluorescent Properties of Crown Ether Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Potassium and Sodium Ions Detection.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 29;11(11):2897. doi: 10.3390/nano11112897. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams PM, Goodie J, Motsinger C D. Treating eating disorders in primary care. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:187–195. - PubMed
-
- Luthra M, Davids MR, Shafiee MA, Halperin ML. Anorexia nervosa and chronic renal insufficiency: a prescription for disaster. QJM. 2004;9:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Takakura S, Nozaki T, Nomura Y, et al. Factors related to renal dysfunction in patients with anorexia nervosa. Eat Weight Disord. 2006;11:73–77. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaelen M, Vanhaelen-Fastre R, But P, Vanherweghem JL. Identification of aristolochic acid in Chinese herbs. Lancet. 1994;343:174. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Rahman EM, Moorthy AV. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) in patients with eating disorders. Clin Nephrol. 1997;47:106–111. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
