Value of Frequency Domain Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Metrics Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation and Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in the Assessment of Brain Tumor-Induced Neurovascular Uncoupling
- PMID: 28657344
- PMCID: PMC5567607
- DOI: 10.1089/brain.2016.0480
Value of Frequency Domain Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Metrics Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation and Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in the Assessment of Brain Tumor-Induced Neurovascular Uncoupling
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Brain Connect 2017;7(6):382-389, DOI:10.1089/brain.2016.0480.Brain Connect. 2017 Sep;7(7):464. doi: 10.1089/brain.2016.0480.correx. Brain Connect. 2017. PMID: 28926301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
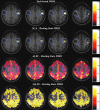
The aim of this study was to explore whether the phenomenon of brain tumor-related neurovascular uncoupling (NVU) in resting-state blood oxygen level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD fMRI) (rsfMRI) may also affect the resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) frequency domain metrics the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and fractional ALFF (fALFF). Twelve de novo brain tumor patients, who underwent clinical fMRI examinations, including task-based fMRI (tbfMRI) and rsfMRI, were included in this Institutional Review Board-approved study. Each patient displayed decreased/absent tbfMRI activation in the primary ipsilesional (IL) sensorimotor cortex in the absence of a corresponding motor deficit or suboptimal task performance, consistent with NVU. Z-score maps for the motor tasks were obtained from general linear model analysis (reflecting motor activation vs. rest). Seed-based correlation analysis (SCA) maps of sensorimotor network, ALFF, and fALFF were calculated from rsfMRI data. Precentral and postcentral gyri in contralesional (CL) and IL hemispheres were parcellated using an automated anatomical labeling template for each patient. Region of interest (ROI) analysis was performed on four maps: tbfMRI, SCA, ALFF, and fALFF. Voxel values in the CL and IL ROIs of each map were divided by the corresponding global mean of ALFF and fALFF in the cortical brain tissue. Group analysis revealed significantly decreased IL ALFF (p = 0.02) and fALFF (p = 0.03) metrics compared with CL ROIs, consistent with similar findings of significantly decreased IL BOLD signal for tbfMRI (p = 0.0005) and SCA maps (p = 0.0004). The frequency domain metrics ALFF and fALFF may be markers of lesion-induced NVU in rsfMRI similar to previously reported alterations in tbfMRI activation and SCA-derived resting-state functional connectivity maps.
Keywords: frequency domain metrics ALFF (amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation) and fALFF (fractional ALFF); motor activation; neurovascular uncoupling; presurgical mapping; resting-state fMRI.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwal S, Sair HI, Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi N, Airan R, Pillai JJ. 2016b. Neurovascular uncoupling in resting state fMRI demonstrated in patients with primary brain gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 43:620–626 - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. 1995. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

