Hesperidin attenuates inflammation and oxidative damage in pleural exudates and liver of rat model of pleurisy
- PMID: 28657497
- PMCID: PMC8900622
- DOI: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1344013
Hesperidin attenuates inflammation and oxidative damage in pleural exudates and liver of rat model of pleurisy
Abstract
Objectives: This study investigated the potential anti-inflammatory effect of hesperidin against carrageenan induced pleurisy in rat model.
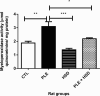
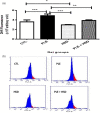
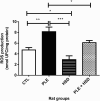
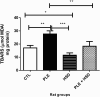
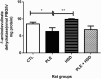
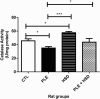
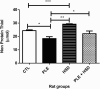
Methods: Twenty-four adult female Wistar rats (350 - 450g) were grouped as follows: Group I: rats were administered saline solution only (Normal control group); Group II: rats were administered saline solution (NaCl 0.9%) orally and injected with carrageenan (Inflammation control group); Group III: rats were administered hesperidin only (Hesperidin group); Group IV: rats were administered hesperidin orally and intrapleurally injected with 2% carrageenan (Inflammation treated with hesperidin group). The exudate volume, total leukocyte count, reactive oxygen species (ROS), myeloperoxidase (MPO),δ-aminolevulinate dehydratase (δ-ALA-D), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), activities as well as non-protein thiol group (NPSH) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels were determined.
Results: Pretreatment with hesperidin at a dose of 80 mg/kg orally per day for 21 days, minimized the increase in pleural exudate volume and leucocyte count and modulated the activities of MPO, SOD and CAT, as well as the levels of ROS, NPSH and TBARS in carrageenan-induced rats.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that hesperidin can elicit its anti-inflammatory action by blocking exudate and leukocyte influx into pleural cavity, inhibiting MPO activity and preventing oxidative damage.
Keywords: Hesperidin; antioxidant enzymes; carrageenan; inflammation; pleural exudate.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hesperidin ameliorates functional and histological outcome and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental stroke.Brain Res. 2011 Oct 28;1420:93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.08.047. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21959178
-
Chronic administration of methionine and/or methionine sulfoxide alters oxidative stress parameters and ALA-D activity in liver and kidney of young rats.Amino Acids. 2017 Jan;49(1):129-138. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2340-y. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Amino Acids. 2017. PMID: 27718024
-
Interferon gamma/interleukin-4 modulation, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of hesperidin in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis model of rats.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020 Oct;42(5):509-520. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2020.1814806. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020. PMID: 32838587
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rat model of pleurisy: The effects of hesperidin on ectoenzymes activity, apoptosis, cell cycle and reactive oxygen species production.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:278-286. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.081. Epub 2017 May 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28460230
-
Radioprotective Effect of Hesperidin: A Systematic Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Jul 12;55(7):370. doi: 10.3390/medicina55070370. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31336963 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of 8 Weeks of 2S-Hesperidin Supplementation on Performance in Amateur Cyclists.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 21;12(12):3911. doi: 10.3390/nu12123911. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33371483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dapagliflozin/Hesperidin Combination Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Alzheimer's Disease in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;16(10):1370. doi: 10.3390/ph16101370. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895841 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperidin protects against IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3721-3727. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6616. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30233731 Free PMC article.
-
Vernonia Amygdalina Del. stimulated glucose uptake in brain tissues enhances antioxidative activities; and modulates functional chemistry and dysregulated metabolic pathways.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Jun;34(3):721-732. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0363-7. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30607820
-
Systems Pharmacology Study of the Anti-Liver Injury Mechanism of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 12;12:618846. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.618846. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33912040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Light RW, Gary Lee YC.. Textbook of pleural diseases. London: Arnold; 2003.
-
- Kass SM, Williams PM, Reamy BV.. Pleurisy. Am Fam Phys. 2007;75:1357–1364. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
