Phytochemicals Targeting Estrogen Receptors: Beneficial Rather Than Adverse Effects?
- PMID: 28657580
- PMCID: PMC5535874
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071381
Phytochemicals Targeting Estrogen Receptors: Beneficial Rather Than Adverse Effects?
Abstract
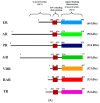
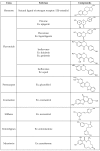
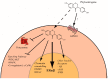
In mammals, the effects of estrogen are mainly mediated by two different estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ. These proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family, characterized by distinct structural and functional domains, and participate in the regulation of different biological processes, including cell growth, survival and differentiation. The two estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes are generated from two distinct genes and have partially distinct expression patterns. Their activities are modulated differently by a range of natural and synthetic ligands. Some of these ligands show agonistic or antagonistic effects depending on ER subtype and are described as selective ER modulators (SERMs). Accordingly, a few phytochemicals, called phytoestrogens, which are synthesized from plants and vegetables, show low estrogenic activity or anti-estrogenic activity with potentially anti-proliferative effects that offer nutraceutical or pharmacological advantages. These compounds may be used as hormonal substitutes or as complements in breast cancer treatments. In this review, we discuss and summarize the in vitro and in vivo effects of certain phytoestrogens and their potential roles in the interaction with estrogen receptors.
Keywords: cancer; cell signaling; epigenetic regulation; estrogen receptor; ligand; selective estrogen receptor modulators; transcription; xenoestrogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Estrogenic and antiestrogenic activities of flavonoid phytochemicals through estrogen receptor binding-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Nutr Cancer. 2000;38(2):229-44. doi: 10.1207/S15327914NC382_13. Nutr Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11525602
-
Comparative study on the nuclear hormone receptor activity of various phytochemicals and their metabolites by reporter gene assays using Chinese hamster ovary cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Feb;32(2):195-202. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.195. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19182375
-
Terpenoids found in the umbelliferae family act as agonists/antagonists for ER(alpha) and ERbeta: differential transcription activity between ferutinine-liganded ER(alpha) and ERbeta.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Feb 22;291(2):354-60. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6446. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 11846412
-
Nuclear and extranuclear-initiated estrogen receptor signaling crosstalk and endocrine resistance in breast cancer.Steroids. 2016 Oct;114:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Steroids. 2016. PMID: 27394959 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor-mediated health benefits of phytochemicals: a review.Food Funct. 2023 Dec 11;14(24):10681-10699. doi: 10.1039/d3fo04702d. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 38047630 Review.
Cited by
-
An isoflavone derivative potently inhibits the angiogenesis and progression of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the MTA2/SerRS/VEGFA pathway.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Aug 15;17(3):693-706. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0010. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32944400 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial and Deleterious Effects of Female Sex Hormones, Oral Contraceptives, and Phytoestrogens by Immunomodulation on the Liver.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 22;20(19):4694. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194694. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31546715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Overview of the Mechanisms of Action of Hormones and Endocrine Disruptor Compounds.Toxics. 2019 Jan 24;7(1):5. doi: 10.3390/toxics7010005. Toxics. 2019. PMID: 30682876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamine Oxidase Expression Is Downregulated by 17β-Estradiol via Estrogen Receptor 2 in Human MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 7;23(14):7521. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147521. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886868 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-food Interactions in the Era of Molecular Big Data, Machine Intelligence, and Personalized Health.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022 Nov 14;13(1):27-50. doi: 10.2174/2212798412666220620104809. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022. PMID: 36173075 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

