Controllable Charge Transfer in Ag-TiO₂ Composite Structure for SERS Application
- PMID: 28657599
- PMCID: PMC5535225
- DOI: 10.3390/nano7070159
Controllable Charge Transfer in Ag-TiO₂ Composite Structure for SERS Application
Abstract
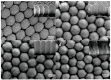
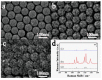
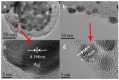
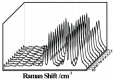
The nanocaps array of TiO₂/Ag bilayer with different Ag thicknesses and co-sputtering TiO₂-Ag monolayer with different TiO₂ contents were fabricated on a two-dimensional colloidal array substrate for the investigation of Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) properties. For the TiO₂/Ag bilayer, when the Ag thickness increased, SERS intensity decreased. Meanwhile, a significant enhancement was observed when the sublayer Ag was 10 nm compared to the pure Ag monolayer, which was ascribed to the metal-semiconductor synergistic effect that electromagnetic mechanism (EM) provided by roughness surface and charge-transfer (CT) enhancement mechanism from TiO₂-Ag composite components. In comparison to the TiO₂/Ag bilayer, the co-sputtered TiO₂-Ag monolayer decreased the aggregation of Ag particles and led to the formation of small Ag particles, which showed that TiO₂ could effectively inhibit the aggregation and growth of Ag nanoparticles.
Keywords: SERS; TiO2-Ag nanocap array; magnetron sputtering; metal-semiconductor composite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Fleischmann M., Hendra P.J., Mcquillan A.J. Raman Spectra of Pyridine Adsorbed at a Silver Electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974;26:163–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1. - DOI
-
- Jeanmaire D.L., Duyne R.P.V. Surface Raman SpectroElectrochemistry Part I. Heterocyclic, Aromatic and Aliphatic Amines Adsorbed on the Anodized Silver Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfac. Electrochem. 1997;84:1–20. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0728(77)80224-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

