Epithelial Deletion of Sulf2 Exacerbates Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury, Inflammation, and Mortality
- PMID: 28657777
- PMCID: PMC5705905
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0367OC
Epithelial Deletion of Sulf2 Exacerbates Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury, Inflammation, and Mortality
Abstract
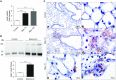
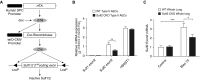
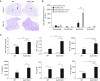
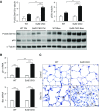
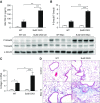
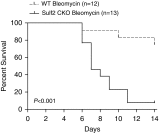
Epithelial injury has been proposed to be the initiating factor in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We have shown previously that heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatase (Sulf) 2 is overexpressed in the hyperplastic type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) in the IPF lungs. By removing 6-O-sulfates from specific heparan sulfate intrachain sites, Sulf2 modulates the functions of many growth factors and cytokines. In this study, we hypothesized that Sulf2 plays a regulatory role in alveolar epithelial injury and repair, using the murine bleomycin model. Consistent with our findings in human IPF lungs, bleomycin treatment in mice resulted in up-regulation of Sulf2 mRNA in whole-lung extracts and overexpression of Sulf2 protein in type II AECs on lung tissue sections. Sulf2 protein was detectable in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid at baseline, and its level was significantly increased after bleomycin exposure. To study the role of Sulf2 in alveolar injury and repair in vivo, we generated a doxycycline-inducible epithelial-specific Sulf2 conditional knockout (Sulf2 CKO) mouse line. After bleomycin exposure, Sulf2 CKO mice exhibited enhanced neutrophil infiltration in the lung, with elevated levels of total protein, lactate dehydrogenase, and cytokines (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and interferon-γ-inducible protein 10) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid compared with wild-type littermates. We further showed that both the p53-p21 DNA damage response and the transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway were up-regulated in Sulf2 CKO mice compared with wild-type. Finally, Sulf2 CKO mice suffered increased mortality after bleomycin exposure. In conclusion, Sulf2 expression in type II AECs plays a protective role in epithelial injury, inflammation and mortality.
Keywords: Sulf2; bleomycin; heparan sulfate; p53; type II alveolar epithelial cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Sulf2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Glycobiology. 2013 Jun;23(6):709-19. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwt010. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Glycobiology. 2013. PMID: 23418199 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase ameliorates lung fibrosis by protecting alveolar epithelial cells against senescence.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 31;294(22):8861-8871. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006615. Epub 2019 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31000627 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Exp Lung Res. 2015 Mar;41(2):57-73. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2014.979516. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Exp Lung Res. 2015. PMID: 25514507 Review.
-
MAP3K19 Is a Novel Regulator of TGF-β Signaling That Impacts Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury and Pulmonary Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2016 May 4;11(5):e0154874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154874. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27144281 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physiology and Pathophysiology of Heparan Sulfate in Animal Models: Its Biosynthesis and Degradation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 10;23(4):1963. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041963. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Carotene enhances the expression of inflammation-related genes and histone H3 K9 acetylation, K4 dimethylation, and K36 trimethylation around these genes in juvenile macrophage-like THP-1 cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Aug 15;31:101325. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101325. eCollection 2022 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 35990579 Free PMC article.
-
A genomic perspective of the aging human and mouse lung with a focus on immune response and cellular senescence.Immun Ageing. 2023 Nov 6;20(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00373-5. Immun Ageing. 2023. PMID: 37932771 Free PMC article.
-
Novel biomarker genes which distinguish between smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with machine learning approach.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Feb 3;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1062-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32013930 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan-6-O-endosulfatase 2, a cancer-related proteoglycan enzyme, is effectively inhibited by a specific sea cucumber fucosylated glycosaminoglycan.Glycobiology. 2025 Apr 23;35(6):cwaf025. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaf025. Glycobiology. 2025. PMID: 40302034
References
-
- Canestaro WJ, Forrester SH, Raghu G, Ho L, Devine BE. Drug treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Chest. 2016;149:756–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

