The Fifth Vital Sign: Postoperative Pain Predicts 30-day Readmissions and Subsequent Emergency Department Visits
- PMID: 28657940
- PMCID: PMC6530481
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002372
The Fifth Vital Sign: Postoperative Pain Predicts 30-day Readmissions and Subsequent Emergency Department Visits
Abstract
Objective: We hypothesized that inpatient postoperative pain trajectories are associated with 30-day inpatient readmission and emergency department (ED) visits.
Background: Surgical readmissions have few known modifiable predictors. Pain experienced by patients may reflect surgical complications and/or inadequate or difficult symptom management.
Methods: National Veterans Affairs Surgical Quality Improvement data on inpatient general, vascular, and orthopedic surgery from 2008 to 2014 were merged with laboratory, vital sign, health care utilization, and postoperative complications data. Six distinct postoperative inpatient patient-reported pain trajectories were identified: (1) persistently low, (2) mild, (3) moderate or (4) high trajectories, and (5) mild-to-low or (6) moderate-to-low trajectories based on postoperative pain scores. Regression models estimated the association between pain trajectories and postdischarge utilization while controlling for important patient and clinical variables.
Results: Our sample included 211,231 surgeries-45.4% orthopedics, 37.0% general, and 17.6% vascular. Overall, the 30-day unplanned readmission rate was 10.8%, and 30-day ED utilization rate was 14.2%. Patients in the high pain trajectories had the highest rates of postdischarge readmissions and ED visits (14.4% and 16.3%, respectively, P < 0.001). In multivariable models, compared with the persistently low pain trajectory, there was a dose-dependent increase in postdischarge ED visits and readmission for pain-related diagnoses, but not postdischarge complications (χ trend P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Postoperative pain trajectories identify populations at risk for 30-day readmissions and ED visits, and do not seem to be mediated by postdischarge complications. Addressing pain control expectations before discharge may help reduce surgical readmissions in high pain categories.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

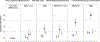
References
-
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. NEngl JMed. 2009;360:1418–1428. - PubMed
-
- Morris MS, Graham LA, Richman JS, et al. Postoperative 30-day readmission: time to focus on what happens outside the hospital. Ann Surg. 2016;264:621 –631. - PubMed
-
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. Patient protection and affordable care act. Public Law. 2010;111:48.
-
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Readmissions reduction program. Available at: http://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpati.... Accessed April 2, 2017.
-
- Jiang HJ, Boutwell AE, Maxwell J, et al. Understanding patient, provider, and system factors related to Medicaid readmissions. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2016;42:115–121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

