Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the lumbar spinal canal: A Case Report With Literature Review
- PMID: 28658093
- PMCID: PMC5500015
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006488
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the lumbar spinal canal: A Case Report With Literature Review
Abstract
Rationale: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare type of mesenchymal tumor. IMT can arise in multiple anatomic locations. IMT of the lumbar spinal canal is exceptionally rare.
Patient concerns: Here, we report the case of a 56-year-old male patient with an IMT who was in good health until 1 year prior to admission, when he began experiencing pain in both lower extremities and the lower back.
Interventions: A space-occupying lesion in the lumbar canal was identified by magnetic resonance imaging and then surgically resected.
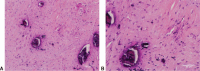
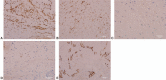
Diagnoses: Histopathological analysis of the lesion revealed a composition of mucous edema, inflammatory cells, collagenous fibers, and spindle cells that were diffuse and positive for smooth muscle actin and CD68; focal positive for vimentin and desmin; and negative for CD34 (marker of vascular endothelial cells), CD21, CD23, CD35, S-100, Epstein-Barr virus infection, Ki-67, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Thus, the diagnosis was an IMT of the lumbar canal.
Outcomes: In the spinal canal, IMT should be considered in the evaluation of tumors although it is a very rare diagnosis. It is a benign lesion, but it has potential for invasion and recurrence.
Lessons: There are no characteristic imaging features of these tumors, but they can be addressed by complete surgical excision. Patients with these lesions should undergo frequent long-term follow-up to detect and address recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Cholvi Calduch R, Fernandez Moreno MC, Diaz-Tobarra M, et al. Hemoperitoneum secondary to perforated inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a case report of an unusual complication. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2016;108:51–2. - PubMed
-
- Cassivi SD, Wylam ME. Pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor associated with histoplasmosis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2006;5:514–6. - PubMed
-
- Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR, et al. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:859–72. - PubMed
-
- Gao F, Zhong R, Li GH, et al. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the head and neck. Acta Radiol 2014;55:434–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

