Application of anterior debridement and reconstruction with anatomical screw-plate fixation for lumbosacral tuberculosis: A 2-year-plus follow-up
- PMID: 28658103
- PMCID: PMC5500025
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007103
Application of anterior debridement and reconstruction with anatomical screw-plate fixation for lumbosacral tuberculosis: A 2-year-plus follow-up
Abstract
This study aimed to determine the efficacy and safety of anterior debridement and reconstruction with anatomical screw-plate fixation in patients with lumbosacral junction tuberculosis (TB).A total of 48 patients (30 males and 18 females) diagnosed with lumbosacral junction TB were included in this study. All patients underwent surgery in our institution from January 2008 to July 2014, using anterior debridement and reconstruction with anatomical screw-plate. Outcome data were evaluated before and after surgery and included lumbosacral angle, Frankel classification, bone fusion, and visual analog scale (VAS) scores.All patients were then followed up for an average of 49.4 months (range, 24-96 months). The mean lumbosacral angle improved from 8.36° ± 5.92° pre-operation to 22.38° ± 4.52° post-operation and 21.13° ± 3.73° during the final follow-up (both P < .05). Solid vertebral fusion was achieved in all patients after 7.6 months on average (range, 6-12 months). No severe complications appeared during operation and post-operation. Neurological performance and VAS scores were significantly improved compared with pre-operation (P < .05).Following standard anti-TB chemotherapy, anterior debridement and reconstruction with anatomical screw-plate fixation may be a feasible and effective therapeutical option for lumbosacral junction TB. This procedure can result in satisfactory bone fusion and deformity correction, and effectively restore lumbosacral junction stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
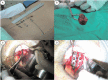

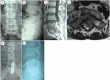
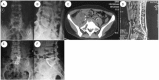
References
-
- China Tuberculosis Control C. The effect of tuberculosis control in China. Lancet 2004;364:417–22. - PubMed
-
- Rajasekaran S, Shanmugasundaram TK, Prabhakar R, et al. Tuberculous lesions of the lumbosacral region: a 15-year follow-up of patients treated by ambulant chemotherapy. Spine 1998;23:1163–7. - PubMed
-
- Pola E, Rossi B, Nasto LA, et al. Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2012;16(suppl 2):79–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

