Endothelial dysfunction in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 28658349
- PMCID: PMC10522258
- DOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000271
Endothelial dysfunction in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to verify the presence of endothelial dysfunction and initial structural atherosclerotic changes in children with Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
Subjects and methods: The study population comprised 31 diabetic children aged 6 to 12 years, divided into two subgroups according to the duration of the T1DM diagnosis: subgroup 1, with less than 5 years elapsed since diagnosis, and subgroup 2, with more than 5 years elapsed since diagnosis. The control group comprised 58 age-matched healthy children. Ultrasonographic techniques were used to measure the flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) of the brachial artery and the intima-media thickness (IMT) of the carotid arteries.
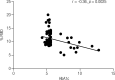
Results: Children with T1DM with longer disease duration showed significantly decreased mean values of FMD compared with those in the control group. No significant differences between the groups were found in relation to IMT. The FMD percentage presented a moderate negative correlation with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting glucose levels.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that endothelial dysfunction may be already present in children with 5 years or more elapsed since diagnosis, even in the absence of atherosclerotic structural changes. The decreased vasodilation response correlated with hyperglycemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Giannini C, Mohn A, Chiarelli F, Kelnar CJH. Macrovascular angiopathy in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011;27(5):436-60. - PubMed
-
- Creager MA, Lüscher TF, Cosentino F, Beckman JA. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences and medical therapy: party l. Circulation. 2003;108(12):1527-32. - PubMed
-
- Calles-Escandon J, Cipolla M. Diabetes and endothelial dysfunction: a clinical perspective. Endocr Rev. 2001;22(1):36-52. - PubMed
-
- Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002;287(19):2570-81. - PubMed
-
- Sheetz MJ, King GI. Molecular understanding of hyperglycemia’s adverse effects for diabetic complications. JAMA. 2002;288(20):2579-88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical