Antipsychotic combinations for schizophrenia
- PMID: 28658515
- PMCID: PMC6481822
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009005.pub2
Antipsychotic combinations for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Many people with schizophrenia do not achieve a satisfactory treatment response with their initial antipsychotic drug treatment. Sometimes a second antipsychotic, in combination with the first, is used in these situations.
Objectives: To examine whether:1. treatment with antipsychotic combinations is effective for schizophrenia; and2. treatment with antipsychotic combinations is safe for the same illness.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's register which is based on regular searches of CINAHL, BIOSIS, AMED, Embase, PubMed, MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and registries of clinical trials. There are no language, time, document type, or publication status limitations for inclusion of records in the register. We ran searches in September 2010, August 2012 and January 2016. We checked for additional trials in the reference lists of included trials.
Selection criteria: We included all randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials comparing antipsychotic combinations with antipsychotic monotherapy for the treatment of schizophrenia and/or schizophrenia-like psychoses.
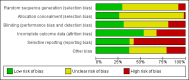
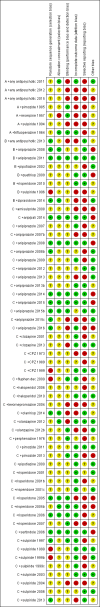
Data collection and analysis: We independently extracted data from the included studies. We analysed dichotomous data using risk ratios (RR) and the 95% confidence intervals (CI). We analysed continuous data using mean difference (MD) with a 95% CIs. For the meta-analysis we used a random-effects model. We used GRADE to complete a 'Summary of findings' table and assessed risk of bias for included studies.
Main results: Sixty-two studies are included in the review, 31 of these compared clozapine monotherapy with clozapine combination. We considered the risk of bias in the included studies to be moderate to high. The majority of trials had unclear allocation concealment, method of randomisation and blinding, and were not free of selective reporting.There is some limited evidence that combination therapy is superior to monotherapy in improving clinical response (RR 0.73, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.85; participants = 2364; studies = 29, very low-quality evidence), although subgroup analyses show that the positive result was due to the studies with clozapine in both the monotherapy and combination groups (RR 0.66, 95% CI 0.53 to 0.83; participants = 1127; studies = 17). Few studies reported on rate of relapse, most likely due to the short length of the studies. Overall, a combination of antipsychotics was not superior or inferior to antipsychotic monotherapy in preventing relapse (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.31 to 1.29; participants = 512; studies = 3, very low-quality evidence), but the pooled data showed high heterogeneity (I² = 82%). A combination of antipsychotics was not superior or inferior to antipsychotic monotherapy in reducing the number of participants discontinuing treatment early (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.07; participants = 3103; studies = 43, low-quality evidence). No difference was found between treatment groups in the number of participants hospitalised (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.36 to 2.55; participants = 202; studies = 3, low-quality evidence) . We did not find evidence of a difference between treatment groups in serious adverse events or those requiring discontinuation (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.69; participants = 2398; studies = 30, very low-quality evidence). There is as lack of evidence on clinically important change in quality of life, with only four studies reporting average endpoint or change data for this outcome on three different scales, none of which showed a difference between treatment groups.
Authors' conclusions: Currently, most evidence regarding the use of antipsychotic combinations comes from short-term trials, limiting the assessment of long-term efficacy and safety. We found very low-quality evidence that a combination of antipsychotics may improve the clinical response. We also found low-quality evidence that a combination of antipsychotics is may make no difference at preventing participants from leaving the study early, preventing relapse and/or causing more serious adverse events than monotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Javier Ortiz‐Orendain – participated in clinical trials sponsored by drug companies but received no payment for his contribution.
Santiago Castiello‐de Obeso ‐ none known.
Luis Enrique Colunga‐Lozano ‐ none known.
Yue Hu ‐ works for Systematic Review Solutions Ltd, a company that carries out systematic reviews.
Nicola Mayaan ‐ worked for Enhance Reviews Ltd during the preparation of this review, a company that carried out systematic reviews mostly for the public sector. Now works for Cochrane Respose.
Clive Adams ‐ none known.
Figures
Update of
-
Antipsychotic combinations for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(2):CD009005. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009005. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 28;6:CD009005. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009005.pub2. PMID: 25267895 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
A +any antipsychotic 2011 {published data only}
A +any antipsychotic 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fricchione Parise V, Balletta G, Addeo L, Manna G. Effectiveness of antipsychotic polypharmacy or monotherapy: real‐world study outcomes. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;22(Suppl 2):323. [DOI: 10.1016/S0924-977X(12)70495-9] - DOI
A +any antipsychotic 2015 {published data only}
-
- Constantine RJ, Andel R, McPherson M, Tandon R. The risks and benefits of switching patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder from two to one antipsychotic medication: a randomized controlled trial. Schizophrenia Research 2015;166(1‐3):194‐200. [DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.05.038] - DOI - PubMed
A +pimozide 1985 {published data only}
-
- Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effects of neuroleptics in symptom‐free schizophrenics: roles of dopaminergic and noradrenergic blockers. Biological Psychiatry 1985;20(11):1161‐6. [0006‐3223: (Print); Nishikawa 1985] - PubMed
A +reserpine 1957 {published data only}
-
- Barrett WW, Ellsworth RB, Clark LD, Enniss J. Study of the differential behavioral effects of reserpine, chlorpromazine, and a combination of these drugs in chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1957; Vol. 18, issue 6:209‐15. [0012‐3714: (Print); Barrett 1957] - PubMed
A +sulpiride 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wang CH, Qin TF, Lin YL, Zhao XF. A clinical effect and following‐up study about sulpiride and clozapine for 105 cases of the schizophrenia type. Journal of Xinxiang Medical College 1994;11(2):148‐51. [MK_007527]
A +trifluoperazine 1964 {published data only}
-
- Talbot DR. Are tranquilizer combinations more effective than a single tranquilizer?. American Journal of Psychiatry 1964;121:597‐600. [0002‐953X: (Print); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
B +any antipsychotic 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hori H, Yoshimura R, Katsuki A, Sugita AI, Atake K, Nakamura J. Switching to antipsychotic monotherapy can improve attention and processing speed, and social activity in chronic schizophrenia patients. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2013;47(12):1843‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.08.024] - DOI - PubMed
B +aripiprazole 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olie JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on body weight and clinical efficacy in schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine:a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;13(8):1115‐25. [DOI: 10.1017/S1461145710000490] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade R, et al. Weight change on aripiprazole‐clozapine combination in schizophrenic patients with weight gain and suboptimal response on clozapine: 16‐week double‐blind study. European Psychiatry 2008;23(Suppl 2):114‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.01.784; 0924‐9338] - DOI
-
- Kriel W. A multicenter, comparative, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled study on the effect on weight of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole in patients with schizophrenia. www.sanctr.gov.za/SAClinicalTrials/tabid/169/Default.aspx (first received 15 November 2006).
-
- Millar H, Felter C, Landsberg W. The effects of aripiprazole in combination with clozapine: patient functioning results from a double‐blind, 16‐week study in patients with schizophrenia (CN138‐170). Journal of Psychopharmacology 2008;22(5):A17. [MEDLINE: ]
B +aripiprazole 2011 {published data only}
B +pipotiazine 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zhu H, Deng D. A study of clozapine combined with or without pipotiazine palmitate in refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine 2002;12:15‐7.
B +quet/risp 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kane JM, Correll CU, Goff DC, Kirkpatrick B, Marder SR, Vester‐Blokland E, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, 16‐week study of adjunctive aripiprazole for schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder inadequately treated with quetiapine or risperidone monotherapy. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2009;70(10):1348‐57. [1555‐2101: (Electronic); DOI: 10.4088/JCP.09m05154yel; Kane 2009] - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCT00325689. A multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, 16 week study of aripiprazole used as dual therapy in the treatment of patients with chronic stable schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00325689?term=NCT00325689&rank=1 (first received May 11 2006). [MEDLINE: ]
B +risperidone 2010 {published data only}
-
- Richardson CM, Feldman S, Kelly DL, Ball MP, Boggs DL, Weiner E, et al. Metabolic side effects of combined antipsychotic treatment: results from a double blind trial of adjunctive risperidone in clozapine treated people with treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2009;35(Suppl 1):38‐9. [MEDLINE: ]
B +sulpiride 1996 {published data only}
-
- Liu QH, Li XL, Zhang YQ, Jin SL, Li ZC, Wang NS, et al. A control study of clozapine in combination with sulpiride in alleviating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry 1996;29(2):87‐90. [MEDLINE: ]
B +ziprasidone 2014 {published data only}
-
- Muscatello MR, Pandolfo G, Mico U, Lamberti Castronuovo E, Abenavoli E, Scimeca G, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with ziprasidone in refractory schizophrenia: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2014;34(1):129‐33. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000042] - DOI - PubMed
C +amisulpride 2008 {published data only}
-
- Assion HJ, Reinbold H, Lemanski S, Basilowski M, Juckel G. Amisulpiride augmentation in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive or unresponsive to clozapine. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2008;41(1):24‐8. [0176‐3679: (Print); DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-993209; Assion 2008] - DOI - PubMed
C +arip/pali 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mayabhate M, Badar V, Somani A. Cognitive and psychomotor effects of adjunctive aripiprazole or paliperidone in patients of schizophrenia receiving olanzapine: a double‐blind placebo controlled clinical study. International Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 2014;3(1):130‐8. [DOI: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20140216] - DOI
C +aripiprazole 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chen HZ, Yu BR, Yang SG, Shen ZX, Mi Q, Jiang YH. Effect of aripiprazole on the hyperprolactinemia caused by sulpiride in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: a clinical observation. Herald of Medicine 2007;26(10):1145‐6. [Chen 2007]
C +aripiprazole 2007b {published data only}
-
- Shim J, Shin J, Kelly DL, Jung D, Seo Y, Conley RR. Adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole for haloperidol induced hyperprolactinemia: double blind, placebo controlled study. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2007;33:460. [Shim 2006 a]
-
- Shim JC, Jae YM, Shin JG, Jung DW, Seo YS, Liu KH, et al. Drug interactions between aripiprazole and haloperidol: double blind placebo controlled study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2007;17:S438. [Shim 2007 d]
-
- Shim JC, Shin JG, Kelly DL, Jung DU, Seo YS, Liu KH, et al. Adjunctive treatment with a dopamine partial agonist, aripiprazole, for antipsychotic‐induced hyperprolactinemia: a placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Psychiatry 2007;164(9):1404‐10. [0002‐953X: (Print); DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06071075; Shim 2006 a1] - DOI - PubMed
C +aripiprazole 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine‐treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Asian Psychiatric Educational Workshop 2007;5:720‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine‐treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69(5):720‐31. [1555‐2101: (Electronic); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chang JS, Lee NY, Ahn YM, Kim YS. The sustained effects of aripiprazole‐augmented clozapine treatment on the psychotic systems and metabolic profiles of patients with refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;32(2):282‐4. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182485871] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim YS. A double‐blind randomized placebo controlled study of aripiprazole augmentation for clozapine‐treated patients with refractory schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00328367?term=NCT00328367&rank=1 (first received 17 May 2006). [MEDLINE: ]
C +aripiprazole 2008b {published data only}
-
- Jin JF, Chao YQ, Xu L, Song ZY, et al. Combined low‐dose aripiprazole improved due to hyperprolactinemia chlorpromazine clinical study [合并小剂量阿立哌唑改善氯丙嗪所致高催乳素血症的临床研究]. Journal of Psychiatry 2008;21(6):455‐6.
C +aripiprazole 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wang L, Zhang B, Xu L, et al. A clinical study on aripiprazole in the treatment of female hyperprolactinemia by haloperidol. China Journal of Health Psychology 2009;17(2):194‐5.
C +aripiprazole 2012 {published data only}
C +aripiprazole 2013 {published data only}
C +aripiprazole 2013b {published data only}
-
- Lee BJ, Lee SJ, Kim MK, Lee JG, Park SW, Kim GM, et al. Effect of aripiprazole on cognitive function and hyperprolactinemia in patients with schizophrenia treated with risperidone. Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 2013; Vol. 11, issue 2:60‐6. [DOI: 10.9758/cpn.2013.11.2.60] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
C +aripiprazole 2014 {published data only}
-
- Chen JX, Zhang RZ, Li W, Liu YH, Jiang LY, Bian QT, et al. Adjunctive treatment of risperidone‐induced hyperprolactinemia with aripiprazole: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Chinese Journal of New Drugs 2014; Vol. 23:811‐4.
C +aripiprazole 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chen JX, Su YA, Bian QT, Wei LH, Zhang RZ, Liu YH, et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole in the treatment of risperidone‐induced hyperprolactinemia: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐response study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015;58:130‐40. [DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.04.011] - DOI - PubMed
C +aripiprazole 2015b {published and unpublished data}
C +aripiprazole 2015c {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR‐IOR‐15006278. Adjunctive aripiprazole treatment for risperidone‐induced hyperprolactinemia: an 8‐week randomized, open‐label, comparative clinical trial. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=10830 (first received 22 April 2015). - PMC - PubMed
C +aripiprazole 2016 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR‐TRC‐14004186. Research of the variance on patients with schizophrenia treated with aripiprazole on hyperprolactinemia induced by risperidone or paliperidone. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=5382. China, (first received 8 January 2014).
C +clozapine 2001 {published data only}
-
- Xie C, Ni XL. The compared study of treating schizophrenia with risperidone combining clozapine. Journal of Preventative Medicine 2001;17(4):245. [MEDLINE: ]
C +clozapine 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jiang L, Lei J, Peng L, et al. Analysis of efficacy of antipsychotics combined with clozapine orally disintegrating tablets in the treatment of schizophrenia with negative symptoms [氯氮平联合抗精神病药治疗精神分裂症阴性 症状的效果分析]. Journal of Bethune Military Medical College 2013;11(4):310‐11.
C +CPZ 1973 {published data only}
C +CPZ 1989 {published data only}
-
- Potter WZ, Ko GN, Zhang LD, Yan WW. Clozapine in China: a review and preview of US/PRC collaboration. Psychopharmacology 1989;99(Suppl):87‐91. [0033‐3158: (Print); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Xu Y. A comparison study on treatment effect of clozapine, chlorpromazine and the combination of clozapine and chlorpromazine in schizophrenia. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1989; Vol. 5, issue 5:306‐8. [MEDLINE: ]
C +CPZ 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cha C, Hui G, Quing G. Evaluation of therapeutic effect with chlorpromazine and clozapine for treatment of schizophrenia. Xinxiang Med Stud 1999;16:311‐6.
C +fluphen dec 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shafti SS. Augmentation of olanzapine by fluphenazine decanoate in poorly responsive schizophrenia. Clinical Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses 2009;3(2):97‐102. [DOI: 10.3371/CSRP.3.2.4] - DOI
C +haloperidol 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mossaheb N, Sacher J, Wiesegger G, Klein N, Spindelegger C, Asenbaum S, et al. Haloperidol in combination with clozapine in treatment‐refractory patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;16(suppl 4):416. [DOI: 10.1016/S0924-977X(06)70524-7] - DOI
C +haloperidol 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lin CH, Kuo CC, Chou LS, Chen YH, Chen CC, Huang KH, et al. A randomized, double‐blind comparison of risperidone versus low‐dose risperidone plus low‐dose haloperidol in treating schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2010;30(5):518‐25. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181f28dff] - DOI - PubMed
C +levomepromazine 2004 {published data only}
-
- Higashima M, Takeda T, Nagasawa T, Hirao N, Oka T, Nakamura M, et al. Combined therapy with low‐potency neuroleptic levomepromazine as an adjunct to haloperidol for agitated patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. European Psychiatry 2004;19(6):380‐1. [0924‐9338: (Print); DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2004.07.001; Higashima 2004] - DOI - PubMed
C +olan/risp 2014 {published data only}
C +olanzapine 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hatta K, Otachi T, Sudo Y, Kuga H, Takebayashi H, Hayashi H, et al. A comparison between augmentation with olanzapine and increased risperidone dose in acute schizophrenia patients showing early non‐response to risperidone. Psychiatry Research 2012;198(2):194‐201. [DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.01.006] - DOI - PubMed
C +olanzapine 2012b {published data only}
C +perphenazine 1976 {published data only}
-
- Yagi G. A double‐blind controlled study on the usefulness of carpipramine‐chlorpromazine combination in the pharmacotherapy of chronic schizophrenic patients. Clincal Evaluation 1976; Vol. 3:351‐403. [MEDLINE: ]
C +pimozide 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bergmann M, Golembo S, Friedman JI, Trammel‐Fisher A, Siever LJ. Pimozide augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00158223?term=NCT00158223&rank=1 (first received 7 September 2005). [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Friedman JI, Lindenmayer JP, Alcantara F, Bowler S, Parak M, White L, et al. Pimozide augmentation of clozapine inpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder unresponsive to clozapine monotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36(6):1289‐95. [DOI: 10.1038/npp.2011.14] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
C +pimozide 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gunduz‐Bruce H. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial response. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00374244?term=Efficacy+of+pimozide+au... (first received 7 September 2006). [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gunduz‐Bruce H. Pimozide for Schizophrenia. Stanley Foundation Research Programs 2009. [MEDLINE: ]
C +pipotiazine 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jia Z, Zhang Z, Jin S. A controlled trial for comparing clozapine combined with pipothiazine palmitate to clozapine alone in the treatment of negative symptoms in schizophrenic patients. Herald of Medicine 2000;19:142‐3.
C +risperidone 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ni J, Jang L, Hong X. Therapeutic effects of clozapine, risperidone and their combination in the treatment of schizophrenia. Health Psychology 2001;3:181‐2.
C +risperidone 2001b {published data only}
-
- Peng H, Kuang Y, Huang X. A control study of risperidone in combination with clozapine in treating refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Modern Clinical Medical Bioengineering 2001;7(2):100‐2. [MEDLINE: ]
C +risperidone 2001c {published data only}
-
- Xin X, Du B, Zeng Z. A controlled clinical study of risperidone and low dose of clozapine in treating schizophrenia. Herald of Medicine 2001;20:501‐2.
C +risperidone 2005 {published data only}
-
- Akdede BB, Anil Yagcioglu AE, Alptekin K, Turgut TI, Tumuklu M, Yazici MK, et al. A double‐blind study of combination of clozapine with risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: effects on cognition. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2006;67(12):1912‐9. [1555‐2101: (Electronic); DOI: 10.4088/JCP.v67n1211; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anil E. Risperidone augmented with clozapine for schizophrenia. Stanley Foundation Research Programs 2009. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Anil Yagcioglu AE, Kivircik Akdede BB, Turgut TI, Tumuklu M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double‐blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2005; Vol. 66, issue 1:63‐72. [0160‐6689: (Print); DOI: 10.4088/JCP.v66n0109; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yagcioglu AEA, Akdede BBK, Turgut TI, Tumuklu M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double‐blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. 24th Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum (CINP); 2004 Jun 20‐24; Paris, France. 2004:63‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
C +risperidone 2005b {published data only}
-
- Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, et al. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. 9th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2003 Mar 29‐Apr 2; Colorado Springs, CO. 2003:130‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, et al. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(1):130‐6. [0002‐953X: (Print); DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.1.130; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
C +risperidone 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gerson SL. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone for refractory schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(17):1846‐8. [1533‐4406: (Electronic); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Grass G, Hellmich M, Leweke FM. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone for refractory schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(17):1846‐8. [1533‐4406: (Electronic); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Honer W. A randomized controlled trial of antipsychotic polypharmacy: clozapine plus risperidone. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2007;17(Suppl 4):S200. [DOI: 10.1016/S0924-977X(07)70237-7; MEDLINE: ] - DOI
-
- Honer W. International study of improving treatment for the most severely ill with schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00272584?term=NCT00272584&rank=1 (first received 3 January 2006). [MEDLINE: ]
C +risperidone 2007 {published data only}
-
- Freudenreich O. Risperidone added to clozapine for schizophrenia. Stanley Foundation Research Programs 2009. [Walsh 2006 b1]
-
- Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Walsh JP, Culhane MA, Goff DC. Risperidone augmentation for schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Schizophrenia Research 2007;92(1‐3):90‐4. [0920‐9964: (Print); DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.12.030; Walsh 2006 b2] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Walsh JP, Freudenreich O, Goff DC. Risperidone augmentation in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00289861?term=NCT00289861&rank=1 (first received 8 February 2006). [MEDLINE: ]
C +sertindole 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nielsen J, Munk‐Jorgensen P. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole ‐ a double blinded randomized placebo study. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00345982?term=NCT00345982&rank=1 (first received 28 June 2006). [Nielsen 2006]
C +sulpiride 1997 {published data only}
-
- Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Radwan M, Schwartz B, Dorfman‐Etrog P, et al. Sulpiride augmentation in people with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;171:569‐73. [0007‐1250: (Print); Shiloh 1997] - PubMed
-
- Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Weizman A. Sulpiride adjunction to clozapine in treatment‐resistant schizophrenic patients: a preliminary case series study. European Psychiatry 1997;12(3):152‐5. [0924‐9338: (Print); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
C +sulpiride 1999 {published data only}
-
- Si S, Yuan C. A comparative trial of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Archives of Psychiatry 1999;12:17‐20.
C +sulpiride 1999b {published data only}
-
- Xao H. A double‐blind comparative study of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Sichuan Mental Health 1999;12:250‐1.
C +sulpiride 1999c {published data only}
-
- Zhu Y, Zhang S, Zhang D. A controlled trial comparing chlorimipramine and sulpiride as adjunct to clozapine in the treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 1999;9(4):204‐5. [MEDLINE: ]
C +sulpiride 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zou G, Huang Y, Zou S, Yang Y. A comparative trial of the beneficial effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Yichun University 2003;25:94‐6.
C +sulpiride 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kotler M, Strous RD, Reznik I, Shwartz S, Weizman A, Spivak B. Sulpiride augmentation of olanzapine in the management of treatment‐resistant chronic schizophrenia: evidence for improvement of mood symptomatology. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2004;19(1):23‐6. [0268‐1315: (Print); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
C +sulpiride 2006 {published data only}
-
- Xu B. Observation on the effect of clozapine and sulpiride on negative symptom schizophrenia patients. China Tropical Medicine 2006;6(5):806.
C +sulpiride 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lin CH, Wang FC, Lin SC, Huang YH, Chen CC, Lane HY. Antipsychotic combination using low‐dose antipsychotics is as efficacious and safe as, but cheaper, than optimal‐dose monotherapy in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;28(5):267‐74. [DOI: 10.1097/YIC.0b013e3283633a83.] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahn 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ahn YM, Kweon YS, Kwon JS, Min SH, Park DB, Yang MJ, et al. The study for switching methods to olanzapine in Korean schizophrenic patients treated with other antipsychotics (II): comparison of safety [항정신병약물 사용 중인 정신분열병 환자에서 올란자핀으로의 교체 방법에 관한 연구: 안전성 비교]. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association 2002;41(5):890‐4.
Alptekin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Alptekin K, Akdede B, Soygur H. TRIES: An open, randomized, prospective, multicenter study, searching the best switch policy of sertindole in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2012;136:S164‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/s0920-9964(12)70519-4] - DOI
Awad 2014 {published data only}
Barbui 2011 {published data only}
-
- Barbui C, Accordini S, Nose M, Stroup S, Purgato M, Girlanda F, et al. Aripiprazole versus haloperidol in combination with clozapine for treatment‐resistant schizophrenia in routine clinical care a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2011;31(3):266‐73. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e318219cba3.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cipriani A, Accordini S, Nose M, Purgato M, Girlanda F, Tansella M, et al. Aripiprazole versus haloperidol in combination with clozapine for treatment‐resistant schizophrenia: a 12‐month, randomized, naturalistic trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;33(4):533‐7. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e318296884f.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nose M, Accordini S, Artioli P, Barale F, Barbui C, Beneduce R, et al. Rationale and design of an independent randomised controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of aripiprazole or haloperidol in combination with clozapine for treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. Trials 2009;10(31):31. [1745‐6215: (Electronic); MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Cazorla 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cazorla P, Mackle M, Zhao J, Ha X, Szegedi A. Safety and tolerability of switching to asenapine from other antipsychotic agents: pooled results from two randomized multicenter trials in stable patients with persistent negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 2012;8:247‐57. [DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S29891] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
ChiCTR‐TRC‐14004854 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR‐TRC‐14004854. A randomized, controlled, multi‐center clinical trial to study the treatment resistant schizophrenia (TRS) in Zhejiang province. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=4719 (first received 26 June 2014).
Citrome 2012 {published data only}
-
- Citrome L, Kianifard F, Meng X, Winseck A, Hochfeld M, Stahl S. Discontinuations following a switch from risperidone, olanzapine, or aripiprazole to iloperidone in patients with schizophrenia: The i‐fans study. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;38(S1):S413‐S4.
Dai 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dai J, Gao H, Sheng J. The effect of synthetical intervention to schizophrenic and hyperlipidemia patients [精神分裂症并发高脂血症患者的综合干预对生活质量的影响]. Medical Journal of Chinese People’s Health 2012;24(5):541‐2. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2012.05.011] - DOI
Dai 2012a {published data only}
-
- Dai T, Xu L, Houzhan L, Chen R, Fan R, Zhao H, et al. Group therapy in combination with antipsychotic medication for the treatment of schizophrenia patients in recovery period [团体治疗联合抗精神病药物对精神分裂症康复期治疗的 效果观察]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use 2012;5(12A):66.
DRKS00008018 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00008018. Are antipsychotics neurotoxic or neuroprotective? A long‐term comparison of two treatment strategies. drks‐neu.uniklinik‐freiburg.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL_ID=DR... (first received 24 April 2015).
Fang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fang M, Chen H, Li LH, Wu R, Li Y, Liu L, et al. Comparison of risperidone oral solution and intramuscular haloperidol with the latter shifting to oral therapy for the treatment of acute agitation in patients with schizophrenia. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;27(2):107‐13. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Fleischhacker 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Sanchez R, Perry PP, Jin N, Peters‐Strickland T, Johnson BR, et al. Aripiprazole once‐monthly for the treatment of schizophrenia: A double‐blind, randomized, non‐inferiority study versus oral aripiprazole. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;38(S1):S339. - PubMed
Fleischhacker 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Sanchez R, Johnson B, Jin N, Forbes RA, McQuade R, et al. Long‐term safety and tolerability of aripiprazole once‐monthly in maintenance treatment of patients with schizophrenia. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;28:171‐6. [DOI: 10.1097/YIC.0b013e3283615dba] - DOI - PubMed
Goff 2008 {published data only}
Henderson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Henderson DC, Fan X, Copeland PM, Sharma B, Borba CP, Boxill R, et al. Aripiprazole added to overweight and obese olanzapine‐treated schizophrenia patients. Joural of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2009;29(2):165‐9. [1533‐712X: (Electronic); DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31819a8dbe; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Hwang 2015 {published data only}
JPRN‐UMIN000011710 {published and unpublished data}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000011710. New Chiba Refractory Schizophrenia Treatment (CREST)‐LAI study: Effectiveness of risperidone long‐acting injectable for treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=JPRN‐UMIN000011710 (first received 2013).
JPRN‐UMIN000012729 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000012729. A comparison of medication adherence of blonanserin and aripiprazole in schizophrenic patients: a multicenter, randomized, open‐label study. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=JPRN‐UMIN000012729 (first received 2013).
JPRN‐UMIN000017047 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000017047. A randomized, open‐label clinical trial on the efficacy of blonanserin and olanzapine in patients with schizophrenia and dopamine supersensitivity psychosis. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=JPRN‐UMIN000017047 (first received 2015).
Kelly 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kelly D, Fischer G, Suppes T. Divalproex extended release and placebo, lithium, or quetiapine for mania. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00183443?term=Divalproex+extended+rel... (first received 13 September 2005). [MEDLINE: ]
Kreinin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kreinin A, Novitski D, Weizman A. Amisulpiride treatment of clozapine‐induced hypersalivation in schizophrenia patients: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled cross‐over study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2006;21:99‐103. - PubMed
Kwon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kwon JS, Mittoux A, Hwang JY, Ong A, Cai ZJ, Su TP. The efficacy and safety of 12 weeks of treatment with sertindole or olanzapine in patients with chronic schizophrenia who did not respond successfully to their previous treatments: A randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, flexible‐dose study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;27(6):326‐35. [DOI: 10.1097/YIC.0b013e32835767a0] - DOI - PubMed
Lerner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lerner V, Libov I, Kotler M, Strous RD. Combination of "atypical" antipsychotic medication in the management of treatment‐resistant schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2004;28(1):89‐98. [0278‐5846: (Print); DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2003.09.024; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Li 2013 {published data only}
-
- Li J. Liqi xingshen method for the treatment of TanQi Yujie type schizophrenia: a random parallel control study [理气醒神方治疗痰气郁结型精神分裂症随机平行对照研究]. Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine 2013;27(5):19‐20. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7813.2013.05(s).84] - DOI
Lieberman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lieberman J, Farr G, Seoane F. TC‐5619 as augmentation therapy to improve cognition in outpatients with cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov (first received 27 October 2009). [MEDLINE: ]
-
- NCT01003379. TC‐5619 as augmentation therapy to improve cognition in outpatients with cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01003379 (first received 27 October 2009). [MEDLINE: ]
Lieberman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lieberman JA, Cutler AJ, Lu K, Laszlovszky I, Migliore R, Durgam S. Cariprazine in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a fixed‐dose phase III, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled trial. CNS Spectrums 2013;18(6):368. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JA, Cutler AJ, Wan S, Migliore R, Ruth A, Laszlovszky I, et al. Cariprazine in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a fixed‐dose, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;23:S477‐8.
Lundbeck 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lundbeck H. A prospective randomised double‐blind parallel‐group active‐controlled cognition study of bifeprunox in schizophrenia (add‐on study to studies 10199 and 10200). www.lundbecktrials.com (first accessed 2004). [MEDLINE: ]
Lundbeck 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lundbeck H. Efficacy study exploring the effect of Lu AE58054 as augmentation therapy in patients with schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00810667?term=Efficacy+study+explorin... (first received 17 December 2008). [MEDLINE: ]
Mantovani 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mantovani C, Labate CM, Sponholz AJ, Azevedo Marques JM, Guapo V G, Simone Brito dos Santos ME, et al. Are low doses of antipsychotics effective in the management of psychomotor agitation? A randomized, rated‐blind trial of four intramuscular interventions. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;33:306‐12. - PubMed
Meltzer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Johnson, Johnson. Randomized, Double‐blind, Placebo‐ and Active‐controlled Parallel Group, Dose‐response Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of 3 Fixed Dosages of Paliperidone Extended Release (6, 9, and 12 mg/Day) and Olanzapine (10 mg/Day) With Open‐label Extension in Treatment of Schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00078039?term=Randomized%2C+Double‐bl... (first received 17 February 2004).
-
- Meltzer H, Bobo W, Nuamah I, Lane R, Hough D, Kramer M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of oral paliperidone extended‐release tablets in the treatment of acute schizophrenia: pooled data from three 6‐week, placebo‐controlled studies. Journal Of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69(5):817‐29. - PubMed
Meltzer 2012 {published data only}
-
- Meltzer HY, Elkis H, Vanover K, Weiner DM, Kammen DP, Peters P, et al. Pimavanserin, a selective serotonin (5‐ht)2a‐inverse agonist, enhances the efficacy and safety of risperidone, 2mg/day, but does not enhance efficacy of haloperidol, 2mg/day: comparison with reference dose risperidone, 6mg/day. Schizophrenia Research 2012;141:144‐52. [DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.07.029.; MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Mi 2013 {published data only}
-
- MI Z, Shi S. Antipsychotic medication combined psychological intervention for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia [药物联合心理干预治疗精神分裂症患者的临床研究]. Chinese Medicine Guide 2013;11(4):505‐6.
Mir 2008 {published data only}
Mythri 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mythri SV, Tharyan P, Sunder S, Kattula D, Kirubakaran R, Adams CE. Rapid tranquillization of violent or agitated patients in a psychiatric emergency setting: Pragmatic, randomized, allocation concealed, participant and assessor blinded trial of intramuscular zuclopenthixol acetate versus intramuscular haloperidol plus promethazine [A comparative study of the effects of an intramuscular injection of zuclopenthixol acetate versus an intramuscular injection of a combination of haloperidol plus promethazine in people with violence or agitation presenting to a psychiatric hospital as an emergency]. Study Protocol (as supplied 2013).
NCT01003379 {published data only}
-
- NCT01003379. TC‐5619 as augmentation therapy to improve cognition in outpatients with cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01003379 (first received 27 October 2009).
NCT01234779 {published data only}
-
- NCT01234779. A study of ro4917838 in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01234779 (first received 3 November 2010).
NCT01939548 {published data only}
-
- NCT01939548. A 12‐week, randomized, phase 2, double‐blind, parallel‐group study of two dose levels of PF‐02545920 compared to placebo in the adjunctive treatment of outpatients with sub‐optimally controlled symptoms of schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01939548 (first received 9 August 2013).
NCT02477670 {published data only}
-
- NCT02477670. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of AVP‐786 for the treatment of residual schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02477670 (first received 18 June 2015).
Pfizer 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pfizer. A study of PF‐03463275 as add‐on therapy in outpatients with persistent negative symptoms of schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00977522?term=A+study+of+PF‐03463275+as+a... (first received 14 September 2009). [MEDLINE: ]
Ruiz‐Doblado 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz‐Doblado S, Baena‐Baldomero A, Esparrago‐Llorca G. Pharmacological augmentation strategies in clozapine‐resistant schizophrenia: Overcoming the resistance. Psiquiatria Biologica 2010;17(3):96‐101. [DOI: 10.1016/j.psiq.2010.07.002] - DOI
Rupnow 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rupnow M, Greenspan A, Kosik‐Gonzalez C, Bossie C, Zhu Y, Gharabawi G, et al. Polypharmacy in schizophrenia: data from a randomized, double‐blind study. 158th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2005 May 21‐26; Atlanta, Georgia, USA. 2005. [MEDLINE: ]
Sacchetti 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sacchetti E, Galluzzo A, Valsecchi P, Romeo F, Gorini B, Warrington L. Comparative efficacy and safety of ziprasidone and clozapine in treatment refractory schizophrenic patients: results of a randomized, double‐blind, 18‐week trial. 13th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia Research; 2006 Feb 4‐10; Davos, Switzerland 2006. [MEDLINE: ]
Semenikhin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Semenikhin DG, Kuchaeva AV, Karpov AM, Mikhailova EB, Murav'eva AV. Additional possibilities for correction of movement disorders induced by neuroleptics in patients with schizophrenia. Zhurnal Nevrologii I Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova 2013;113(11):78‐80. - PubMed
Sofronov 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sofronov A, Spikina A, Savelyev A. The role of modern antipsychotics in correction of neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia patients. European Psychiatry 2013;28:1247. [DOI: 10.1016/S0924-9338(13)76320-X] - DOI
Spyker 2015 {published data only}
Stahl 2010b {published data only}
-
- Stahl S, Cucchiaro J, Simonelli D, Loebel A. Long‐term safety and tolerability of lurasidone in subjects with schizophrenia: results of a 6‐month, open‐label study. 49th Annual meeting of the Americam College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 5‐9 December 2010; Miami, Florida. 2010.
Sukegawa 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sukegawa T, Ito T, Hasegawa M, Mizuno Y, Inagaki A, Sakamoto H, et al. A randomized controlled trial on the dose reduction and simplification for polypharmacy of antipsychotics. Tottori Journal of Clinical Research 2008;1(1):169‐81.
Sukegawa 2014 {published data only}
UMIN000004931 {published data only}
-
- UMIN000004931. An intervention study of optimizing algorism‐based pharmacological treatment for schizophrenia. www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/index.htm (first received 22 January 2011).
Wang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wang W, Chen H, Zhao L. Antipsychotic medication combined with acupuncture therapy for the treatment of schizophrenia [抗精神病药物联合针刺治疗精神分裂症 60 例疗效分析]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Health 2013;25(10):63‐4. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2013.10.043] - DOI
Weiden 2013 {published data only}
-
- Weiden PJ, Citrome L, Glick ID, Alva G, Winseck A, Kianifard F, et al. Initial 2‐week outcomes following 2 methods of switching to iloperidone from risperidone in patients with schizophrenia. CNS Spectrums 2013;18(6):348.
Wilson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wilson WH. Open clozapine treatment following a controlled clinical trial of lithium augmentation of haloperidol for refractory schizophrenia. Lithium 1994;5(2):113‐4.
Winseck 2013 {published data only}
-
- Winseck A, Glick ID, Weiden PJ, Citrome L, Alva G, Kianifard F, et al. Initial 2‐week outcomes following 2 methods of switching to iloperidone from aripiprazole in patients with schizophrenia. CNS Spectrums 2013;18(6):362‐3.
Wu 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wu L. A control study of risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Health Psychology 2002;10:135‐7.
Wu 2015 {published data only}
-
- 吴士玲, 张金香. Clinical study of aripiprazole combined with ziprasidone for schizophrenia [阿立哌唑结合齐拉西酮治疗精神分裂症的临床护理观察]. 全国高血压防治知识推广培训班暨健康血压中国行福建漳州会 2015;22(1):145.
Xia 2014 {published data only}
-
- Xia SY, Zhang YR, Yu H, Meng X, Zhang P, Liu J. Treatment of antipsychotic drug‐induced phlegm dampness type amenorrhea by Wuji Powder and a small dose aripiprazole: a clinical study. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 2014;34(12):1440‐3. - PubMed
Xu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Xu. Clinical observation of sertraline combined with sulpiride for first onset schizophrenia [舍曲林合并舒必利治疗首发精神分裂症临床观察]. Ningxia Medical Journal [宁夏医学杂志] 2008;30(6):542‐3.
Yamanouchi 2015 {published data only}
-
- UMIN000004511. The clinical study to correct multiple and large amount of administering to antipsychotic safely and effectively. www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/index.htm (first received 10 November 2010).
-
- Yamanouchi Y, Sukegawa T, Inagaki A, Inada T, Yoshio T, Yoshimura R, et al. Evaluation of the individual safe correction of antipsychotic agent polypharmacy in Japanese patients with chronic schizophrenia: validation of safe corrections for antipsychotic polypharmacy and the high‐dose method. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;18:5. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Yue 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yue H, Song L, Xu Y. A comparative trial of risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia over two years. Shangai Archive of Psychiatry 2004;16:165‐7.
Zhang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Wang J, Zhang Z. Shugan‐Jieyu capsule combined with antipsychotics for the treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia [舒肝解郁胶囊合并抗精神病药物治疗精神分裂症阴性症状的疗效]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2012;10(4):228‐9.
Zhang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhang B, Chang L. Venlafaxine combined antipsychotics in the treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia [文拉法辛联合抗精神病药治疗精神分裂症阴性症状疗效分析]. Shanxi Medical Journal 2013;42(6):685‐6.
Zink 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kuwilsky A, Krumm B, Englisch S, Dressing H, Zink M. Long‐term efficacy and tolerability of clozapine combined with ziprasidone or risperidone. Pharmacopsychiatry 2010;43(6):216‐20. - PubMed
-
- Zink M. Clozapine‐augmentation with ziprasidone or risperidone, a randomized, prospective trial. www.clinicaltrials.gov (first received 15 September 2005). [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Zink M, Kuwilsky A, Krumm B, Dressing H. Efficacy and tolerability of ziprasidone versus risperidone as augmentation in patients partially responsive to clozapine: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2009;23(3):305‐14. [0269‐8811: (Print); MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT01450514 {published data only}
-
- NCT01450514. Proof‐of‐concept study of pipamperone 15mg added to stable risperidone or paliperidone treatment in chronic schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients with residual symptoms: a Phase I/IIa, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of 7 weeks. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01450514 (first received 7 October 2011).
Xu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Xu L, Ji Jue H, Shi H. A control study of aripiprazole in the treatment of hyperprolactinemia by antipsychotics origin [阿立呱哩治疗抗精神病药物所致 高催乳素血症对照研究]. Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science 2006;15(8):718‐20.
Yuan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Han X, Yuan YB, Yu X. The Chinese first‐episode schizophrenia trial: Background and study design [中國首發精神分裂症臨床試驗(CNFEST):背景和研究設計]. East Asian Archives of Psychiatry 2014;24:169‐73. - PubMed
-
- Yuan Y, Yang F, Lu Z, Wang CY, Deng H, Zhao J, et al. Effectiveness of three atypical antipsychotic‐initiated treatments in chinese first‐episode schizophrenia: An open randomized clinical trial. Schizophrenia Research 2014;153(Suppl. 1):S218. [DOI: 10.1016/S0920-9964(14)70628-0] - DOI
References to ongoing studies
CTRI‐02‐003397 {published data only}
-
- CTRI‐02‐003397. Efficacy of Aripiprazole adjunctive treatment on body weight, metabolic parameters, clinical efficacy, and adverse events in people with psychotic disorders on treatment with Clozapine. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. www.ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=5862 (first received 14 February 2013).
ISRCTN68824876 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN68824876. Amisulpiride augmentation in clozapine‐unresponsive schizophrenia. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN68824876 (first received 2 March 2010).
-
- NCT01246232. Amisulpiride augmentation in clozapine‐unresponsive schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01246232 (first received 22 November 2010).
Schmidt‐Kraepelin 2013 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00003603. A randomized double‐blind controlled trial to assess the benefits of olanzapine and amisulpiride combination treatment in acutely ill schizophrenia patients ‐ COMBINE. ichgcp.net/clinical‐trials‐registry/NCT01609153 (first received 1 June 2012).
-
- NCT01609153. A randomized double‐blind controlled trial to assess the benefits of olanzapine and amisulpride combination treatment in acutely ill schizophrenia patients ‐ COMBINE. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01609153 (first received 23 May 2012). - PubMed
-
- Schmidt‐Kraepelin C. A RCT to assess the benefits of olanzapine and amisulpride combination treatment (COMBINE): design and methods. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2013;263(Suppl. 1):S15‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
Ahmed 1998
-
- Ahmed I, Soares KV, Seifas R, Adams CE. Randomized controlled trials in Archives of General Psychiatry (1959‐1995): a prevalence study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1998;55(8):754‐5. [PUBMED: 9707389] - PubMed
Altman 1996
Andreasen 1983
-
- Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS). Iowa City, Iowa: University of Iowa, 1983.
Andreasen 1984
-
- Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS). Iowa City, Iowa: University of Iowa, 1984.
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc., 2000.
APA 2013
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM‐5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013. [DOI: 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596] - DOI
Barber 2017
Barnes 1989
-
- Barnes TRE. A rating scale for drug‐induced akathisia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:672‐6. - PubMed
Begg 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276(8):637‐9. [PUBMED: 8773637] - PubMed
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use [Apercu sur la problematique des indices d'efficacite therapeutique, 3: comparaison des indices et utilisation. Groupe d'Etude des Indices D'efficacite]. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. [PUBMED: 10667106] - PubMed
CADTH 2012
Centorrino 2005
Chouinard 1980
-
- Chouinard G, Ross‐Chouinard A, Annable L, Jones BD. The extrapyramidal symptom rating scale. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1980;7:233.
Correll 2009
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28; Cape Town. Cape Town: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2000.
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled clinical trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtina F, Worthingtond HV, Vaile A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Endicott 1976
-
- Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiss JL, Cohen J. The Global Assessment Scale: A procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Archives of General Psychiatry 1976;33(6):766‐71. - PubMed
Freudenreich 2002
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(7):7‐10. - PubMed
Gaebel 2005
Gallego 2009
-
- Gallego JA, Bonetti J, Zhang J, Kane JM, Correll CU. Prevalence and correlates of antipsychotic polypharmacy: A systematic review and meta‐regression of global and regional trends from the 1970s to 2009. Schizophrenia Research 2012;138(1):18‐28. [DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.03.018] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gangluy 2004
Gardner 2010
Grunder 2009
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy U. Early Clinical Drug Evaluation (ECDEU) Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. National Institute of Mental Health, 1976.
Hasan 2012
-
- Hasan A, Falkai P, Wobrock T, Lieberman J, Glenthoj B, Gattaz WF, et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia, part 1: update 2012 on the acute treatment of schizophrenia and the management of treatment resistance. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry 2012;13(5):318‐78. [DOI: 10.3109/15622975.2012.696143] - DOI - PubMed
Heinrich 1984
-
- Heinrich DW, Hanlon TE, Carpenter WT. The quality of life scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1984;10:388‐98. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Jääskeläinen 2012
Kapur 2001
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kay 1987
-
- Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1987;13(2):261‐76. - PubMed
Kim 2002
-
- Kim JH, Jung HD, Kang UG, Jeong SH, Ahn YM, Byun HJ, et al. Metric characteristics of the drug‐induced extrapyramidal symptoms scale (DIEPSS): A practical combined rating scale for drug‐induced movement disorders. Movement Disorders 2002;17:1354‐9. - PubMed
Kirkpatrick 2006
Leon 2006
-
- Leon AC, Mallinckrodt CH, Chuang‐Stein C, Archibald DG, Archer GE, Chartier K. Attrition in randomized controlled clinical trials: methodological issues in psychopharmacology. Biological Psychiatry 2006;59(11):1001‐5. [PUBMED: 16905632] - PubMed
Leucht 2005
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79(2‐3):231‐8. [PUBMED: 15982856] - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of brief psychiatric rating scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. [PUBMED: 16199797] - PubMed
Lingjaerde 1987
-
- Lingjaerde O, Ahlfors UG, Bech P, Dencker SJ, Elgen K. The UKU side effect rating scale. A new comprehensive rating scale for psychotropic drugs and across‐sectional study of side effects in neuroleptic‐treated patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1987;334(Suppl.):1‐100. - PubMed
Magalhães 2016
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
McGrath 2008
Meader 2014
Meltzer 2000
-
- Meltzer HY, Kostakoglu AE. Combining antipsychotics: is there evidence for efficacy?. Psychiatric Times 2000;17:25‐34.
Meng 2015
-
- Meng M, Li W, Zhang S, Wang HY, Sheng JH, Wang J, et al. Using aripiprazole to reduce antipsychotic‐induced hyperprolactinemia: meta‐analysis of currently available randomized controlled trials. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry 2015;27(1):4‐17. [DOI: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.215014] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Misawa 2011
Naber 1995
-
- Naber D. A self‐rating to measure subjective effects of neuroleptic drugs. Relationships to objective psychopathology, quality of life, compliance and other clinical variables. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1995;10:133‐8. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:790‐812.
Paton 2008
Rupnow 2007
-
- Rupnow MF, Greenspan A, Gharabawi GM, Kosik‐Gonzalez C, Zhu Y, Stahl SM. Incidence and costs of polypharmacy: data from a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of risperidone and quetiapine in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2007;23(11):2815‐22. [DOI: 10.1185/030079907X233359] - DOI - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1970;(Suppl 212):11‐9. - PubMed
Sommer 2012
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D, editor(s). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Taylor 2009
-
- Taylor DM, Smith L. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic‐‐a meta‐analysis of randomized, placebo‐controlled studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2009;119(6):419‐25. [PUBMED: 19245679] - PubMed
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
Waddington 1998
-
- Waddington JL, Youssef HA, Kinsella A. Mortality in schizophrenia. Antipsychotic polypharmacy and absence of adjunctive anticholinergics over the course of a 10‐year prospective study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1998;173:325‐9. - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐Item short‐form health survey (SF‐36®): I. conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473‐83. - PubMed
Weiden 1999
-
- Weiden PJ, Casey DE. "Polypharmacy": Combining antipsychotic medications in the treatment of schizophrenia. Journal of Practical Psychiatry and Behavioral Health 1999;5:229‐33.
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

