Microfluidic Formation of Monodisperse Coacervate Organelles in Liposomes
- PMID: 28658517
- PMCID: PMC5601218
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201703145
Microfluidic Formation of Monodisperse Coacervate Organelles in Liposomes
Abstract
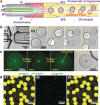
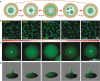
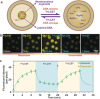
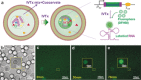
Coacervates have been widely studied as model compartments in protocell research. Complex coacervates composed of disordered proteins and RNA have also been shown to play an important role in cellular processes. Herein, we report on a microfluidic strategy for constructing monodisperse coacervate droplets encapsulated within uniform unilamellar liposomes. These structures represent a bottom-up approach to hierarchically structured protocells, as demonstrated by storage and release of DNA from the encapsulated coacervates as well as localized transcription.
Keywords: artificial organelles; coacervates; liposomes; microfluidics; phase transitions.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complex coacervates as artificial membraneless organelles and protocells.Biomicrofluidics. 2020 Sep 1;14(5):051301. doi: 10.1063/5.0023678. eCollection 2020 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2020. PMID: 32922586 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Based Coacervates as a Model for Membraneless Organelles: Formation, Properties, and Interfacial Liposome Assembly.Langmuir. 2016 Oct 4;32(39):10042-10053. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02499. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Langmuir. 2016. PMID: 27599198
-
pH-Controlled Coacervate-Membrane Interactions within Liposomes.ACS Nano. 2020 Apr 28;14(4):4487-4498. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b10167. Epub 2020 Apr 7. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32239914 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacing Coacervates with Membranes: From Artificial Organelles and Hybrid Protocells to Intracellular Delivery.Small Methods. 2023 Dec;7(12):e2300294. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202300294. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Small Methods. 2023. PMID: 37354057 Review.
-
Protein intrinsic disorder-based liquid-liquid phase transitions in biological systems: Complex coacervates and membrane-less organelles.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Jan;239:97-114. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 31. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 27291647 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid sponge droplets as programmable synthetic organelles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 4;117(31):18206-18215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004408117. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32694212 Free PMC article.
-
Protocells Capable of Generating a Cytoskeleton-like Structure from intracellular Membrane-active Artificial Organelles.Adv Funct Mater. 2023 Dec 8;33(50):2306904. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202306904. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Adv Funct Mater. 2023. PMID: 38344241 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid in Chips: A Brief Review of Liposomes Formation by Microfluidics.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Nov 3;16:7391-7416. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S331639. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34764647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aqueous Triple-Phase System in Microwell Array for Generating Uniform-Sized DNA Hydrogel Particles.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 23;12:705022. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.705022. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34367260 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of stabilized droplets from liquid-liquid phase separation for higher-order structures and functions.Commun Chem. 2024 Apr 9;7(1):79. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01168-5. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 38594355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- None
-
- van der Gucht J., Spruijt E., Lemmers M., Cohen Stuart M. A., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 407–422; - PubMed
-
- Priftis D., Tirrell M., Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9396–9405;
-
- Kizilay E., Kayitmazer A. B., Dubin P. L., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 24–37; - PubMed
-
- Spruijt E., Westphal A. H., Borst J. W., Cohen Stuart M. A., van der Gucht J., Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6476–6484.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

