PLX8394, a new generation BRAF inhibitor, selectively inhibits BRAF in colonic adenocarcinoma cells and prevents paradoxical MAPK pathway activation
- PMID: 28659148
- PMCID: PMC5490236
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0684-x
PLX8394, a new generation BRAF inhibitor, selectively inhibits BRAF in colonic adenocarcinoma cells and prevents paradoxical MAPK pathway activation
Abstract
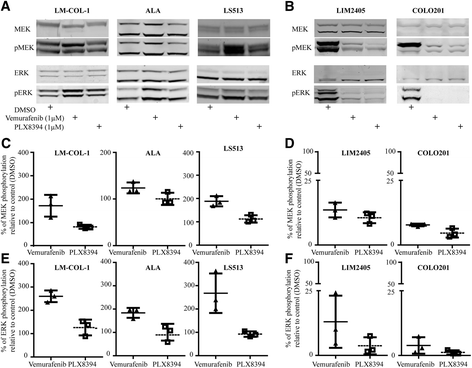
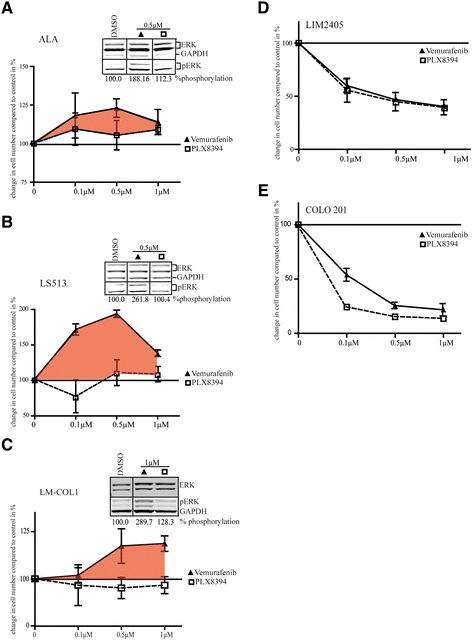
BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) are standard of care for the treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-driven metastatic melanoma, but can lead to paradoxical activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway. This can result in the promotion of precancerous lesions and secondary neoplasms, mainly (but not exclusively) associated with pre-existing mutations in RAS genes. We previously reported a patient with synchronous BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma and BRAF wt /KRAS G12D-metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), whose CRC relapsed and progressed when treated with the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436). We used tissue from the resected CRC metastasis to derive a cell line, LM-COL-1, which directly and reliably mimicked the clinical scenario including paradoxical activation of the MAPK signalling pathway resulting in increased cell proliferation upon dabrafenib treatment. Novel BRAF inhibitors (PLX8394 and PLX7904), dubbed as "paradox breakers", were developed to inhibit V600 mutated oncogenic BRAF without causing paradoxical MAPK pathway activation. In this study we used our LM-COL-1 model alongside multiple other CRC cell lines with varying mutational backgrounds to demonstrate and confirm that the paradox breaker PLX8394 retains on-target inhibition of mutated BRAF V600 without paradoxically promoting MAPK signalling.
Keywords: BRAF; Colorectal cancer; MAPK pathway; Melanoma; Paradoxical activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All research involving human participants or tissue carried out at the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute is conducted under the guidelines of the Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of the Austin Health Office for Research. The HREC conforms with the National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research (NHMRC, ARC, UA, 2007, National Statement) and is constituted in accordance with the requirements of the National Health & Medical Research Council (NHMRC). Both committees operate under strict Terms of Reference and Standard Operating procedures.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BRAF paradox breakers PLX8394, PLX7904 are more effective against BRAFV600Ε CRC cells compared with the BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 and shown by detailed pathway analysis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Apr 1;1867(4):166061. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.166061. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33385518
-
RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation.Nature. 2015 Oct 22;526(7574):583-6. doi: 10.1038/nature14982. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26466569
-
Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinase BRAF-mutant lung cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):13456-13461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610456113. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27834212 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Mar;11(3):285-95. doi: 10.2174/187152011795347469. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21426297 Review.
-
[Cellular and molecular mechanisms of carcinogenic side effects and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in metastatic melanoma with BRAFV600 mutation: state of the knowledge].Ann Pathol. 2013 Dec;33(6):375-85. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Ann Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24331719 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Mutational Landscape of Bystander Cells: Drug-Promoted Blood Cancer From High-Prevalence Pre-neoplasias in Patients on BRAF Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 11;10:540030. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.540030. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33042833 Free PMC article.
-
A CRAF/glutathione-S-transferase P1 complex sustains autocrine growth of cancers with KRAS and BRAF mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 11;117(32):19435-19445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000361117. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32719131 Free PMC article.
-
The N6-methyladenosine modification of circALG1 promotes the metastasis of colorectal cancer mediated by the miR-342-5p/PGF signalling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 19;21(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01560-6. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35305647 Free PMC article.
-
N-(7-Cyano-6-(4-fluoro-3-(2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)acetamido)phenoxy)benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide (TAK632) Promotes Inhibition of BRAF through the Induction of Inhibited Dimers.J Med Chem. 2018 Jun 14;61(11):5034-5046. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00499. Epub 2018 May 18. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29727562 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an anoikis-related gene signature and prognostic model for predicting the tumor microenvironment and response to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 May 8;15:1378305. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378305. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38779664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halaban R, Zhang W, Bacchiocchi A, Cheng E, Parisi F, Ariyan S, et al. PLX4032, a selective BRAF(V600E) kinase inhibitor, activates the ERK pathway and enhances cell migration and proliferation of BRAF melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010;23:190–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2010.00685.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

