ERCC1-XPF endonuclease-positioned to cut
- PMID: 28659377
- PMCID: PMC5509994
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201797489
ERCC1-XPF endonuclease-positioned to cut
Abstract
To counteract damage to our genomes, numerous endo‐ and exonucleases incise the DNA backbone to remove damaged and aberrant DNA structures. It is imperative that such incisions be very tightly controlled, as unwanted DNA breaks are a key source of genome instability. Two new papers in The EMBO Journal shed light on how the activity of one such nuclease—ERCC1‐XPF, an enzyme involved in various DNA repair pathways—is regulated to perform incision in the vicinity of DNA interstrand crosslinks.
Figures
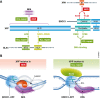
Comment on
-
Recruitment and positioning determine the specific role of the XPF-ERCC1 endonuclease in interstrand crosslink repair.EMBO J. 2017 Jul 14;36(14):2034-2046. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695223. Epub 2017 Mar 14. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28292785 Free PMC article.
-
RPA activates the XPF-ERCC1 endonuclease to initiate processing of DNA interstrand crosslinks.EMBO J. 2017 Jul 14;36(14):2047-2060. doi: 10.15252/embj.201796664. Epub 2017 Jun 12. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28607004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogliolo M, Schuster B, Stoepker C, Derkunt B, Su Y, Raams A, Trujillo JP, Minguillon J, Ramirez MJ, Pujol R, Casado JA, Banos R, Rio P, Knies K, Zuniga S, Benitez J, Bueren JA, Jaspers NG, Schärer OD, de Winter JP et al (2013) Mutations in ERCC4, encoding the DNA‐repair endonuclease XPF, cause Fanconi anemia. Am J Hum Genet 92: 800–806 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dehe PM, Gaillard PH (2017) Control of structure‐specific endonucleases to maintain genome stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18: 315–330 - PubMed
-
- Guervilly JH, Takedachi A, Naim V, Scaglione S, Chawhan C, Lovera Y, Despras E, Kuraoka I, Kannouche P, Rosselli F, Gaillard PH (2015) The SLX4 complex is a SUMO E3 ligase that impacts on replication stress outcome and genome stability. Mol Cell 57: 123–137 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

