Deubiquitylation of deubiquitylases
- PMID: 28659380
- PMCID: PMC5493773
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.170016
Deubiquitylation of deubiquitylases
Abstract
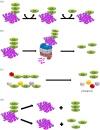
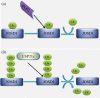
Deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the ubiquitylation of target proteins, thereby regulating diverse cellular functions. In contrast to the plethora of research being conducted on the ability of DUBs to counter the degradation of cellular proteins or auto-ubiquitylated E3 ligases, very little is known about the mechanisms of DUB regulation. In this review paper, we summarize a novel possible mechanism of DUB deubiquitylation by other DUBs. The available data suggest the need for further experiments to validate and characterize this notion of 'Dubbing DUBs'. The current studies indicate that the idea of deubiquitylation of DUBs by other DUBs is still in its infancy. Nevertheless, future research holds the promise of validation of this concept.
Keywords: auto-regulation; deubiquitylating DUBs; proteasome degradation; self-deubiquitylation; ubiquitylation.
© 2017 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ye Y, et al. 2010. TRE17/USP6 oncogene translocated in aneurysmal bone cyst induces matrix metalloproteinase production via activation of NFκB. Oncogene 29, 3619–3629. (doi:10.1038/onc.2010.116) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen C, Ye Y, Robertson SE, Lau AW, Mak D-OD, Chou MM. 2005. Calcium/calmodulin regulates ubiquitination of the ubiquitin-specific protease TRE17/USP6. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 35 967–35 973. (doi:10.1074/jbc.M505220200) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. 2006. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22, 159–180. (doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010605.093503) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alonso-de Vega I, Martín Y, Smits VA. 2014. USP7 controls Chk1 protein stability by direct deubiquitination. Cell Cycle 13, 3921–3926. (doi:10.4161/15384101.2014.973324) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nicholson B, Suresh Kumar KG. 2011. The multifaceted roles of USP7: new therapeutic opportunities. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 60, 61 (doi:10.1007/s12013-011-9185-5) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
