Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
- PMID: 28659587
- PMCID: PMC5489510
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04559-y
Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 26;8(1):9889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28151-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29941876 Free PMC article.
Abstract
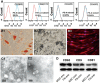
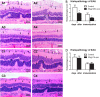
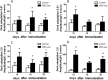
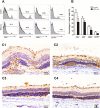
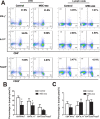
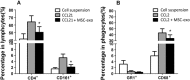
We previously demonstrated that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) ameliorated experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in rats. Recently, MSC-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) were thought to carry functions of MSCs. In this study, we tested the effect of local administration of human MSC-Exo on established EAU in the same species. Rats with EAU induced by immunization with interphotoreceptor retinol-binding protein 1177-1191 peptide were treated by periocular injections of increasing doses of MSC-Exo starting at the disease onset for 7 consecutive days. The in vitro effects of MSC-Exo on immune cell migration and responder T cell proliferation were examined by chemotactic assays and lymphocyte proliferation assays, respectively. We found that MSC-Exo greatly reduced the intensity of ongoing EAU as their parent cells by reducing the infiltration of T cell subsets, and other inflammatory cells, in the eyes. Furthermore, the chemoattractive effects of CCL2 and CCL21 on inflammatory cells were inhibited by MSC-Exo. However, no inhibitory effect of MSC-Exo on IRBP-specific T cell proliferation was observed. These results suggest that MSC-Exo effectively ameliorate EAU by inhibiting the migration of inflammatory cells, indicating a potential novel therapy of MSC-Exo for uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

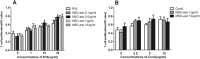
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

