Response to Interleukin-1 Inhibitors in 140 Italian Patients with Adult-Onset Still's Disease: A Multicentre Retrospective Observational Study
- PMID: 28659802
- PMCID: PMC5469286
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00369
Response to Interleukin-1 Inhibitors in 140 Italian Patients with Adult-Onset Still's Disease: A Multicentre Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
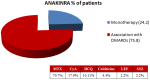
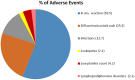
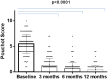
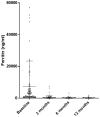
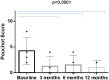
Background: Interleukin (IL)-1 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of Adult onset Still's disease (AOSD). Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of anakinra (ANA) and canakinumab (CAN) in a large group of AOSD patients. Methods: Data on clinical, serological features, and concomitant treatments were retrospectively collected at baseline and after 3, 6, and 12 months from AOSD patients (Yamaguchi criteria) referred by 18 Italian centers. Pouchot's score was used to evaluate disease severity. Results: One hundred forty patients were treated with ANA; 4 were subsequently switched to CAN after ANA failure. The systemic pattern of AOSD was identified in 104 (74.2%) of the ANA-treated and in 3 (75%) of the CAN-treated groups; the chronic-articular type of AOSD was identified in 48 (25.8%) of the ANA-treated and in 1 (25%) of the CAN-treated groups. Methotrexate (MTX) was the most frequent disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) used before beginning ANA or CAN [91/140 (75.8%), 2/4 (50%), respectively]. As a second-line biologic DMARD therapy in 29/140 (20.7%) of the patients, ANA was found effective in improving all clinical and serological manifestations (p < 0.0001), and Pouchot's score was found to be significantly reduced at all time points (p < 0.0001). No differences in treatment response were identified in the ANA-group when the patients were stratified according to age, sex, disease pattern or mono/combination therapy profile. ANA primary and secondary inefficacy at the 12-month time point was 15/140 (10.7%) and 11/140 (7.8%), respectively. Adverse events (AEs) [mainly represented by in situ (28/47, 59.5%) or diffuse (12/47, 25.5%) skin reactions and infections (7/47, 14.8%)] were the main causes for discontinuation. Pouchot's score and clinical and serological features were significantly ameliorated at all time points (p < 0.0001) in the CAN-group, and no AEs were registered during CAN therapy. Treatment was suspended for loss of efficacy only in one case (1/4, 25%). Conclusion: This is the largest retrospective observational study evaluating the efficacy and safety of IL-1 inhibitors in AOSD patients. A good response was noted at 3 months after therapy onset in both the ANA- and CAN-groups. Skin reaction may nevertheless represent a non-negligible AE during ANA treatment.
Keywords: Adult-onset Still’s disease; anakinra; canakinumab; interleukin (IL)-1; treatment.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

