A Complex Endomembrane System in the Archaeon Ignicoccus hospitalis Tapped by Nanoarchaeum equitans
- PMID: 28659892
- PMCID: PMC5468417
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01072
A Complex Endomembrane System in the Archaeon Ignicoccus hospitalis Tapped by Nanoarchaeum equitans
Abstract
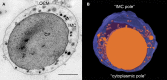
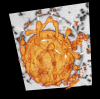
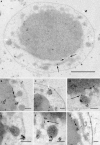
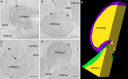
Based on serial sectioning, focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM), and electron tomography, we depict in detail the highly unusual anatomy of the marine hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon, Ignicoccus hospitalis. Our data support a complex and dynamic endomembrane system consisting of cytoplasmic protrusions, and with secretory function. Moreover, we reveal that the cytoplasm of the putative archaeal ectoparasite Nanoarchaeum equitans can get in direct contact with this endomembrane system, complementing and explaining recent proteomic, transcriptomic and metabolomic data on this inter-archaeal relationship. In addition, we identified a matrix of filamentous structures and/or tethers in the voluminous inter-membrane compartment (IMC) of I. hospitalis, which might be responsible for membrane dynamics. Overall, this unusual cellular compartmentalization, ultrastructure and dynamics in an archaeon that belongs to the recently proposed TACK superphylum prompts speculation that the eukaryotic endomembrane system might originate from Archaea.
Keywords: 3D; Archaea; FIB/SEM; electron tomography; eukaryogenesis; membranes; symbiosis; ultrastructure.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The unusual cell biology of the hyperthermophilic Crenarchaeon Ignicoccus hospitalis.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2012 Aug;102(2):203-19. doi: 10.1007/s10482-012-9748-5. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2012. PMID: 22653377 Review.
-
Ignicoccus hospitalis and Nanoarchaeum equitans: ultrastructure, cell-cell interaction, and 3D reconstruction from serial sections of freeze-substituted cells and by electron cryotomography.Arch Microbiol. 2008 Sep;190(3):395-408. doi: 10.1007/s00203-008-0402-6. Epub 2008 Jul 12. Arch Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18622597 Free PMC article.
-
Life on the edge: functional genomic response of Ignicoccus hospitalis to the presence of Nanoarchaeum equitans.ISME J. 2015 Jan;9(1):101-14. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.112. Epub 2014 Jul 11. ISME J. 2015. PMID: 25012904 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of a Crenarchaeal ATP Synthase in the Light of the Unique Bioenergetics of Ignicoccus Species.J Bacteriol. 2019 Mar 13;201(7):e00510-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00510-18. Print 2019 Apr 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30642991 Free PMC article.
-
Happy together: genomic insights into the unique Nanoarchaeum/Ignicoccus association.J Biol. 2009;8(1):7. doi: 10.1186/jbiol110. Epub 2009 Jan 23. J Biol. 2009. PMID: 19216728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell genomics of co-sorted Nanoarchaeota suggests novel putative host associations and diversification of proteins involved in symbiosis.Microbiome. 2018 Sep 17;6(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0539-8. Microbiome. 2018. PMID: 30223889 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation and Competition Were Primary Driving Forces for Biological Evolution.Microb Physiol. 2025;35(1):13-29. doi: 10.1159/000544890. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Microb Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39999802 Review.
-
Targeted isolation and cultivation of uncultivated bacteria by reverse genomics.Nat Biotechnol. 2019 Nov;37(11):1314-1321. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0260-6. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Nat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31570900 Free PMC article.
-
The Syntrophy hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotes revisited.Nat Microbiol. 2020 May;5(5):655-667. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0710-4. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32341569 Review.
-
Multisubstrate specificity shaped the complex evolution of the aminotransferase family across the tree of life.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 25;121(26):e2405524121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2405524121. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38885378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff M., Magelhaes P., Ram S. (2004). Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Intern. 11, 36–42.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

