Metal complexes as potential modulators of inflammatory and autoimmune responses
- PMID: 28660015
- PMCID: PMC5472922
- DOI: 10.1039/c4sc03094j
Metal complexes as potential modulators of inflammatory and autoimmune responses
Abstract
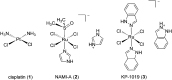
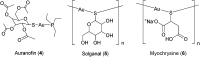
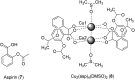
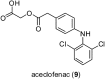
Over the past few decades, the realm of inorganic medicinal chemistry has been dominated by the study of the anti-cancer properties of transition metal complexes, particularly those based on platinum or ruthenium. However, comparatively less attention has been focused on the development of metal complexes for the treatment of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases. Metal complexes possess a number of advantages that render them as attractive alternatives to organic small molecules for the development of therapeutic agents. In this perspective, we highlight recent examples in the development of transition metal complexes as modulators of inflammatory and autoimmune responses. The studies presented here serve to highlight the potential of transition metal complexes in modulating inflammatory or immune pathways in cells.
Figures
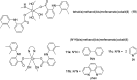
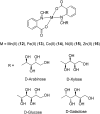
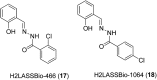
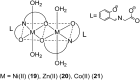





Similar articles
-
Group 9 organometallic compounds for therapeutic and bioanalytical applications.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Dec 16;47(12):3614-31. doi: 10.1021/ar500310z. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25369127
-
Rhodium complexes as therapeutic agents.Dalton Trans. 2016 Feb 21;45(7):2762-71. doi: 10.1039/c5dt04338g. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Dalton Trans. 2016. PMID: 26743935 Review.
-
Recent development of transition metal complexes with in vivo antitumor activity.J Inorg Biochem. 2017 Dec;177:276-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 16. J Inorg Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28641893 Review.
-
The development of anticancer ruthenium(ii) complexes: from single molecule compounds to nanomaterials.Chem Soc Rev. 2017 Oct 2;46(19):5771-5804. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00195a. Chem Soc Rev. 2017. PMID: 28654103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward Multi-Targeted Platinum and Ruthenium Drugs-A New Paradigm in Cancer Drug Treatment Regimens?Chem Rev. 2019 Jan 23;119(2):1058-1137. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00271. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30640441 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel family of small molecule HIF-1 alpha stabilizers for the treatment of diabetic wounds; an integrated in silico, in vitro, and in vivo strategy.RSC Adv. 2022 Nov 1;12(48):31293-31302. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05364k. eCollection 2022 Oct 27. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36349012 Free PMC article.
-
Polyoxometalates: metallodrug agents for combating amyloid aggregation.Natl Sci Rev. 2024 Jun 28;11(7):nwae226. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae226. eCollection 2024 Jul. Natl Sci Rev. 2024. PMID: 39081537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Antiplatelet Activity Relationships of Novel Ruthenium (II) Complexes: Investigation of Its Molecular Targets.Molecules. 2018 Feb 22;23(2):477. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020477. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29470443 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroglutamate aminopeptidase 1 may be an indicator of cellular inflammatory response as revealed using a sensitive long-wavelength fluorescent probe.Chem Sci. 2016 Jul 1;7(7):4694-4697. doi: 10.1039/c6sc00951d. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 30155117 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of TQ-6, a Novel Ruthenium-Derivative Compound, against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced In Vitro Macrophage Activation and Liver Injury in Experimental Mice: The Crucial Role of p38 MAPK and NF-κB Signaling.Cells. 2018 Nov 19;7(11):217. doi: 10.3390/cells7110217. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30463239 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

