The Number of Positive Tumor Marker Status Is Beneficial for the Selection of Therapeutic Modalities in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 28660154
- PMCID: PMC5472937
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2016.00055
The Number of Positive Tumor Marker Status Is Beneficial for the Selection of Therapeutic Modalities in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
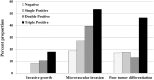
Hepatic resection (HR) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are popular local therapies for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Alpha-fetoprotein, Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein, and des-c-carboxy prothrombin are well-known and useful tumor markers for HCC. The positive number status of these tumor markers has recently been demonstrated as beneficial for predicting outcome for HCC patients treated with local therapy. Although the normal ranges reported have differed by institution, the positivity of tumor markers is consistent and can easily be assessed. Kumamoto and Wakayama's group clearly demonstrated the following: 1) Regardless of the degree of tumor stage, a triple-positive tumor marker profile can predict poor outcome in HCC patients undergoing HR; 2) For RFA alone, HCC patients with double- and triple-positive status, having less than three lesions and lesions ≤3 cm in diameter show comparably insufficient outcomes; 3) For HCC patients with lesions ≤5 cm in Child-Pugh grade A, HR is preferred over RFA; 4) Microvascular invasion rates increased even in the double-positive patients, while poorly differentiated HCC was frequently observed only in the triple-positive patients; and 5) RFA with chemoembolization, anatomical liver resection, and postoperative adjuvant chemoembolization or hepatic arterial chemotherapy might improve the outcome for patients with highly malignant HCC with multiple positive tumor markers. However, the impacts of these therapies still need to be evaluated in prospective comparative studies.
Keywords: Alpha-fetoprotein; Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin; Double-positive tumor markers; Hepatic resection; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Lens culinaris agglutinin reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein; Radiofrequency ablation; Triple-positive tumor markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- Cho YK, Kim JK, Kim WT, Chung JW. Hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for very early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a Markov model analysis. Hepatology. 2010;51:1284–1290. doi: 10.1002/hep.23466. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Makuuchi M, Izumi N, Ichida T, Kudo M, et al. Comparison of resection and ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a cohort study based on a Japanese nationwide survey. J Hepatol. 2013;58:724–729. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.11.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imai K, Beppu T, Chikamoto A, Doi K, Okabe H, Hayashi H, et al. Comparison between hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation as first-line treatment for solitary small-sized hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Hepatol Res. 2013;43:853–864. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Toyoda H, Kumada T, Kiriyama S, Sone Y, Tanikawa M, Hisanaga Y, et al. Prognostic significance of simultaneous measurement of three tumor markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Tangkijvanich P, Anukulkarnkusol N, Suwangool P, Lertmaharit S, Hanvivatvong O, Kullavanijaya P, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis based on serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;31:302–308. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources