Oral Supplementation of Melatonin Protects against Fibromyalgia-Related Skeletal Muscle Alterations in Reserpine-Induced Myalgia Rats
- PMID: 28661421
- PMCID: PMC5535882
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071389
Oral Supplementation of Melatonin Protects against Fibromyalgia-Related Skeletal Muscle Alterations in Reserpine-Induced Myalgia Rats
Abstract
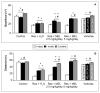
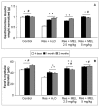
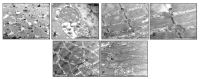
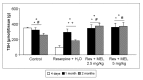
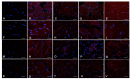
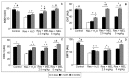
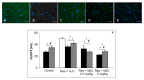
Fibromyalgia is a chronic syndrome characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain and an extensive array of other symptoms including disordered sleep, fatigue, depression and anxiety. Important factors involved in the pathogenic process of fibromyalgia are inflammation and oxidative stress, suggesting that ant-inflammatory and/or antioxidant supplementation might be effective in the management and modulation of this syndrome. Recent evidence suggests that melatonin may be suitable for this purpose due to its well known ant-inflammatory, antioxidant and analgesic effects. Thus, in the current study, the effects of the oral supplementation of melatonin against fibromyalgia-related skeletal muscle alterations were evaluated. In detail, 90 Sprague Dawley rats were randomly treated with reserpine, to reproduce the pathogenic process of fibromyalgia and thereafter they received melatonin. The animals treated with reserpine showed moderate alterations at hind limb skeletal muscles level and had difficulty in moving, together with significant morphological and ultrastructural alterations and expression of inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in the gastrocnemius muscle. Interestingly, melatonin, dose and/or time dependently, reduced the difficulties in spontaneous motor activity and the musculoskeletal morphostructural, inflammatory, and oxidative stress alterations. This study suggests that melatonin in vivo may be an effective tool in the management of fibromyalgia-related musculoskeletal morphofunctional damage.
Keywords: fibromyalgia; inflammation; melatonin; oxidative stress; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired mitochondrial quality control in fibromyalgia: Mechanisms involved in skeletal muscle alteration.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024 Aug;758:110083. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110083. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38969196
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Skeletal Muscle of a Fibromyalgia Model: The Potential Benefits of Melatonin.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):765. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030765. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754674 Free PMC article.
-
A novel GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator, ASP8062, exerts analgesic effects in a rat model of fibromyalgia.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 15;865:172750. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172750. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31647906
-
Benefits of dietary phytochemical supplementation on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage: Is including antioxidants enough?Nutrition. 2015 Sep;31(9):1072-82. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26233864 Review.
-
Impact of Melatonin on Skeletal Muscle and Exercise.Cells. 2020 Jan 24;9(2):288. doi: 10.3390/cells9020288. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31991655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pioglitazone improves skeletal muscle functions in reserpine-induced fibromyalgia rat model.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):1032-1040. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1916069. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34233552 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and Comorbidities in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Curr Dev Disord Rep. 2018;5(3):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s40474-018-0147-0. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Curr Dev Disord Rep. 2018. PMID: 30148039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Underpinnings of Musculoskeletal Pain During Treatment With Aromatase Inhibitors for Breast Cancer: A Biological Pathway Analysis.Biol Res Nurs. 2020 Apr;22(2):263-276. doi: 10.1177/1099800419895114. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Biol Res Nurs. 2020. PMID: 31847542 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin as a Coadjuvant in the Treatment of Patients with Fibromyalgia.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 12;11(7):1964. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071964. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of P2X7 Purinergic Receptor Ameliorates Fibromyalgia Syndrome by Suppressing NLRP3 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 16;22(12):6471. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126471. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34208781 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

