Glycosylation of Recombinant Antigenic Proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: In Silico Prediction of Protein Epitopes and Ex Vivo Biological Evaluation of New Semi-Synthetic Glycoconjugates
- PMID: 28661444
- PMCID: PMC6152100
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22071081
Glycosylation of Recombinant Antigenic Proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: In Silico Prediction of Protein Epitopes and Ex Vivo Biological Evaluation of New Semi-Synthetic Glycoconjugates
Abstract
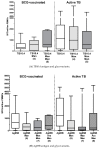
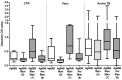
Tuberculosis is still one of the most deadly infectious diseases worldwide, and the use of conjugated antigens, obtained by combining antigenic oligosaccharides, such as the lipoarabinomannane (LAM), with antigenic proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), has been proposed as a new strategy for developing efficient vaccines. In this work, we investigated the effect of the chemical glycosylation on two recombinant MTB proteins produced in E. coli with an additional seven-amino acid tag (recombinant Ag85B and TB10.4). Different semi-synthetic glycoconjugated derivatives were prepared, starting from mannose and two disaccharide analogs. The glycans were activated at the anomeric position with a thiocyanomethyl group, as required for protein glycosylation by selective reaction with lysines. The glycosylation sites and the ex vivo evaluation of the immunogenic activity of the different neo-glycoproteins were investigated. Glycosylation does not modify the immunological activity of the TB10.4 protein. Similarly, Ag85B maintains its B-cell activity after glycosylation while showing a significant reduction in the T-cell response. The results were correlated with the putative B- and T-cell epitopes, predicted using a combination of in silico systems. In the recombinant TB10.4, the unique lysine is not included in any T-cell epitope. Lys30 of Ag85B, identified as the main glycosylation site, proved to be the most important site involved in the formation of T-cell epitopes, reasonably explaining why its glycosylation strongly influenced the T-cell activity. Furthermore, additional lysines included in different epitopes (Lys103, -123 and -282) are also glycosylated. In contrast, B-cell epitopic lysines of Ag85B were found to be poorly glycosylated and, thus, the antibody interaction of Ag85B was only marginally affected after coupling with mono- or disaccharides.
Keywords: MTB recombinant antigens; epitope; glycoconjugate vaccines; neo-glycoproteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monitoring antigenic protein integrity during glycoconjugate vaccine synthesis using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016 Sep;408(22):6123-32. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9723-5. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016. PMID: 27372716 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope and affinity determination of recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ag85B antigen towards anti-Ag85 antibodies using proteolytic affinity-mass spectrometry and biosensor analysis.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Jan;411(2):439-448. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1466-z. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30498982
-
Rational design of multiple TB antigens TB10.4 and TB10.4-Ag85B as subunit vaccine candidates against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Pharm Res. 2010 Feb;27(2):224-34. doi: 10.1007/s11095-009-9995-y. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 19862606
-
The role of glycosylation in protein antigenic properties.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Mar;59(3):445-55. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8437-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 11964123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterial glycoproteins: a novel subset of vaccine candidates.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Sep 17;4:133. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00133. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25279354 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Lipoarabinomannan in Active and Passive Protection Against Tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 11;10:1968. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01968. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of glycosylation on the affinity of the MTB protein Ag85B for specific antibodies: towards the design of a dual-acting vaccine against tuberculosis.Biol Direct. 2024 Jan 25;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00454-5. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 38268026 Free PMC article.
-
Glycovaccine Design: Optimization of Model and Antitubercular Carrier Glycosylation via Disuccinimidyl Homobifunctional Linker.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 23;15(5):1321. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051321. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242563 Free PMC article.
-
Biocatalyzed Synthesis of Glycostructures with Anti-infective Activity.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Sep 6;55(17):2409-2424. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00136. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35942874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational design, preparation and characterization of recombinant Ag85B variants and their glycoconjugates with T-cell antigenic activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.RSC Adv. 2018 Jun 26;8(41):23171-23180. doi: 10.1039/c8ra03535k. eCollection 2018 Jun 21. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seghrouchni F., Contini S., Markova R., Drenska R., Sadki K., Baassi L., Todorova Y., Terzieva V., Bocchino M., Cappelli G., et al. Design of immunogenic peptides from M. tuberculosis genes expressed during macrophage infection. Tuberculosis. 2009;89:210–217. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2009.03.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

