Quantitative determination of free D-Asp, L-Asp and N-methyl-D-aspartate in mouse brain tissues by chiral separation and Multiple Reaction Monitoring tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 28662080
- PMCID: PMC5491048
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179748
Quantitative determination of free D-Asp, L-Asp and N-methyl-D-aspartate in mouse brain tissues by chiral separation and Multiple Reaction Monitoring tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
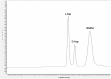
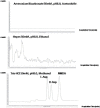
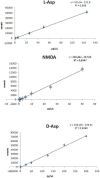
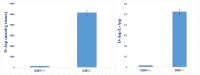
Several studies have suggested that free d-Asp has a crucial role in N-methyl d-Asp receptor-mediated neurotransmission playing very important functions in physiological and pathological processes. This paper describes the development of an analytical procedure for the direct and simultaneous determination of free d-Asp, l-Asp and N-methyl d-Asp in specimens of different mouse brain tissues using chiral LC-MS/MS in Multiple Reaction Monitoring scan mode. After comparing three procedures and different buffers and extraction solvents, a simple preparation procedure was selected the analytes of extraction. The method was validated by analyzing l-Asp, d-Asp and N-methyl d-Asp recovery at different spiked concentrations (50, 100 and 200 pg/μl) yielding satisfactory recoveries (75-110%), and good repeatability. Limits of detection (LOD) resulted to be 0.52 pg/μl for d-Asp, 0.46 pg/μl for l-Asp and 0.54 pg/μl for NMDA, respectively. Limits of quantification (LOQ) were 1.57 pg/μl for d-Asp, 1.41 pg/μl for l-Asp and 1.64 pg/μl for NMDA, respectively. Different concentration levels were used for constructing the calibration curves which showed good linearity. The validated method was then successfully applied to the simultaneous detection of d-Asp, l-Asp and NMDA in mouse brain tissues. The concurrent, sensitive, fast, and reproducible measurement of these metabolites in brain tissues will be useful to correlate the amount of free d-Asp with relevant neurological processes, making the LC-MS/MS MRM method well suited, not only for research work but also for clinical analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determination of melatonin in Acyrthosiphon pisum aphids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Insect Physiol. 2016 Mar;86:48-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 15. J Insect Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26778054
-
Simultaneous quantification of labeled (2)H5-glycerol, (13)C6-glucose, and endogenous D-glucose in mouse plasma using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Nov;407(28):8617-22. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9015-5. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26362155
-
Determination of thyroid hormones in mouse tissues by isotope-dilution microflow liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Oct 15;1033-1034:413-420. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.08.037. Epub 2016 Aug 26. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27649501
-
Determination of trichothecenes A (T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, and diacetoxyscirpenol) in the tissues of broilers using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 30;942-943:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.10.034. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24231141 Review.
-
D-Amino acids in protein: The mirror of life as a molecular index of aging.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018 Jul;1866(7):840-847. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018. PMID: 29530565 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Aspartic Acid with Co3O4-ZnO Nanorods Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;13(1):88. doi: 10.3390/bios13010088. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671923 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Relative Quantification of hFSH Glycoforms in Women's Sera via MS-PRM-Based Approach.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 27;13(6):798. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060798. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34071747 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Polyphenols and Metals in Chinese Tea Infusions by Mass Spectrometry.Foods. 2020 Jun 25;9(6):835. doi: 10.3390/foods9060835. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32630507 Free PMC article.
-
D-Amino Acids and D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides: Potential Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets?Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 18;11(11):1716. doi: 10.3390/biom11111716. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple-Reaction Monitoring Tandem Mass Method for Determination of Phenolics and Water-Soluble Vitamins in Eccoilopus formosanus.Molecules. 2020 Aug 10;25(16):3632. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163632. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32785047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radkov AD, Moe LA. Bacterial synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98: 5363–5374. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5726-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moe LA. Amino acids in the rhizosphere: from plants to microbes. Am J Bot. 2013;100: 1692–1705. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1300033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jia C, Lietz CB, Yu Q, Li L. Site-Specific Characterization of D-Amino Acid Containing Peptide Epimers by Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2014;86: 2972–2981. doi: 10.1021/ac4033824 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Livnat I, Tai HC, Jansson ET, Bai L, Romanova EV, Chen TT, et al. A d-Amino Acid-Containing Neuropeptide Discovery Funnel. Anal Chem. 2016;88: 11868–11876. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03658 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai L, Sheeley S, Sweedler JV. Analysis of Endogenous D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides in Metazoa. Bioanal Rev. 2009;1: 7–24. doi: 10.1007/s12566-009-0001-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

