Electrical risk score beyond the left ventricular ejection fraction: prediction of sudden cardiac death in the Oregon Sudden Unexpected Death Study and the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
- PMID: 28662567
- PMCID: PMC5837238
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx331
Electrical risk score beyond the left ventricular ejection fraction: prediction of sudden cardiac death in the Oregon Sudden Unexpected Death Study and the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract
Aims: There is an urgent need to extend sudden cardiac death (SCD) risk stratification beyond the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). We evaluated whether a cumulative electrocardiogram (ECG) risk score would improve identification of individuals at high risk of SCD.
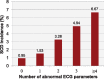
Methods and results: In the community-based Oregon Sudden Unexpected Death Study (catchment population ∼1 million), 522 SCD cases with archived 12-lead ECG available (65.3 ± 14.5 years, 66% male) were compared with 736 geographical controls to assess the incremental value of multiple ECG parameters in SCD prediction. Heart rate, LV hypertrophy, QRS transition zone, QRS-T angle, QTc, and Tpeak-to-Tend interval remained significant in the final model, which was externally validated in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Sixteen percent of cases and 3% of controls had ≥4 abnormal ECG markers. After adjusting for clinical factors and LVEF, increasing ECG risk score was associated with progressively greater odds of SCD. Overall, subjects with ≥4 ECG abnormalities had an odds ratio (OR) of 21.2 for SCD [95% confidence interval (CI) 9.4-47.7; P < 0.001]. In the LVEF >35% subgroup, the OR was 26.1 (95% CI 9.9-68.5; P < 0.001). The ECG risk score increased the C-statistic from 0.625 to 0.753 (P < 0.001), with net reclassification improvement of 0.319 (P < 0.001). In the ARIC cohort validation, risk of SCD associated with ≥4 ECG abnormalities remained significant after multivariable adjustment (hazard ratio 4.84; 95% CI 2.34-9.99; P < 0.001; C-statistic improvement 0.759-0.774; P = 0.019).
Conclusion: This novel cumulative ECG risk score was independently associated with SCD and was particularly effective for LVEF >35% where risk stratification is currently unavailable. These findings warrant further evaluation in prospective clinical investigations.
Keywords: Death; Electrocardiography; Left ventricular ejection fraction; Prevention; Risk stratification; Sudden cardiac.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2017. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Comment in
-
Signalling the risk of sudden cardiac death: the ECG and beyond.Eur Heart J. 2017 Oct 21;38(40):3026-3028. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx420. Eur Heart J. 2017. PMID: 29020236 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després J-P, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB.. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016;133:e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- Priori SG, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen K, Kuck KH, Hernandez-Madrid A, Nikolaou N, Norekval TM, Spaulding C, Van Veldhuisen DJ; Authors/Task Force M, Document R. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J 2015;36:2793–2867. - PubMed
-
- Deo R, Norby FL, Katz R, Sotoodehnia N, Adabag S, DeFilippi CR, Kestenbaum B, Chen LY, Heckbert SR, Folsom AR, Kronmal RA, Konety S, Patton KK, Siscovick D, Shlipak MG, Alonso A.. Development and validation of a sudden cardiac death prediction model for the general population. Circulation 2016;134:806–816. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122492/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

