Lipid Droplets in Health and Disease
- PMID: 28662670
- PMCID: PMC5492776
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0521-7
Lipid Droplets in Health and Disease
Abstract
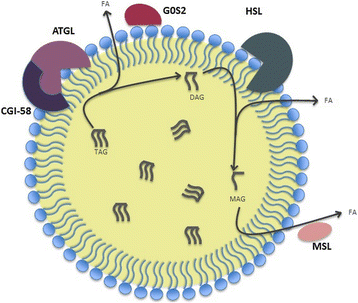
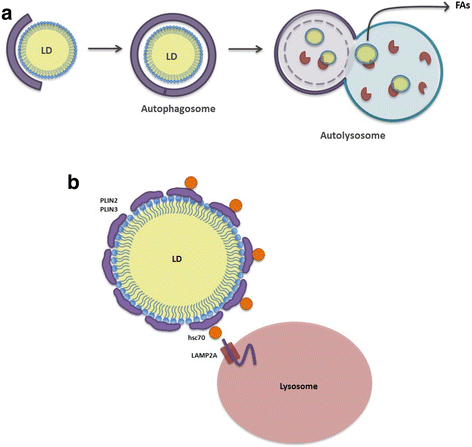
Lipids are essential building blocks synthesized by complex molecular pathways and deposited as lipid droplets (LDs) in cells. LDs are evolutionary conserved organelles found in almost all organisms, from bacteria to mammals. They are composed of a hydrophobic neutral lipid core surrounding by a phospholipid monolayer membrane with various decorating proteins. Degradation of LDs provide metabolic energy for divergent cellular processes such as membrane synthesis and molecular signaling. Lipolysis and autophagy are two main catabolic pathways of LDs, which regulate lipid metabolism and, thereby, closely engaged in many pathological conditons. In this review, we first provide an overview of the current knowledge on the structural properties and the biogenesis of LDs. We further focus on the recent findings of their catabolic mechanism by lipolysis and autophagy as well as their connection ragarding the regulation and function. Moreover, we discuss the relevance of LDs and their catabolism-dependent pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: Lipid droplets; chaperone-mediated autophagy; lipolysis; lipophagy.
Figures


References
-
- Greenberg AS, Egan JJ, Wek SA, Garty NB, Blanchette-Mackie E, Londos C. Perilipin, a major hormonally regulated adipocyte-specific phosphoprotein associated with the periphery of lipid storage droplets. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:11341–11346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

