Wbp2nl has a developmental role in establishing neural and non-neural ectodermal fates
- PMID: 28663133
- PMCID: PMC5554722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.06.025
Wbp2nl has a developmental role in establishing neural and non-neural ectodermal fates
Abstract
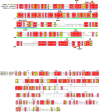
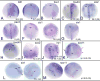
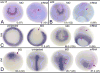
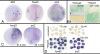
In many animals, maternally synthesized mRNAs are critical for primary germ layer formation. In Xenopus, several maternal mRNAs are enriched in the animal blastomere progenitors of the embryonic ectoderm. We previously identified one of these, WW-domain binding protein 2 N-terminal like (wbp2nl), that others previously characterized as a sperm protein (PAWP) that promotes meiotic resumption. Herein we demonstrate that it has an additional developmental role in regionalizing the embryonic ectoderm. Knock-down of Wbp2nl in the dorsal ectoderm reduced cranial placode and neural crest gene expression domains and expanded neural plate domains; knock-down in ventral ectoderm reduced epidermal gene expression. Conversely, increasing levels of Wbp2nl in the neural plate induced ectopic epidermal and neural crest gene expression and repressed many neural plate and cranial placode genes. The effects in the neural plate appear to be mediated, at least in part, by down-regulating chd, a BMP antagonist. Because the cellular function of Wbp2nl is not known, we mutated several predicted motifs. Expressing mutated proteins in embryos showed that a putative phosphorylation site at Thr45 and an α-helix in the PH-G domain are required to ectopically induce epidermal and neural crest genes in the neural plate. An intact YAP-binding motif also is required for ectopic epidermal gene expression as well as for down-regulating chd. This work reveals novel developmental roles for a cytoplasmic protein that promotes epidermal and neural crest formation at the expense of neural ectoderm.
Keywords: Neural crest; Neural plate; PAWP; Placodes; foxd3; zic2.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential distribution of competence for panplacodal and neural crest induction to non-neural and neural ectoderm.Development. 2012 Mar;139(6):1175-87. doi: 10.1242/dev.074468. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Development. 2012. PMID: 22318231
-
Specific induction of cranial placode cells from Xenopus ectoderm by modulating the levels of BMP, Wnt, and FGF signaling.Genesis. 2015 Oct;53(10):652-9. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22881. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Genesis. 2015. PMID: 26249012
-
The requirement of histone modification by PRDM12 and Kdm4a for the development of pre-placodal ectoderm and neural crest in Xenopus.Dev Biol. 2015 Mar 1;399(1):164-176. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.12.028. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25576027
-
Establishing the pre-placodal region and breaking it into placodes with distinct identities.Dev Biol. 2014 May 1;389(1):13-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Setting appropriate boundaries: fate, patterning and competence at the neural plate border.Dev Biol. 2014 May 1;389(1):2-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.027. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24321819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi- and Transgenerational Effects of Developmental Exposure to Environmental Levels of PFAS and PFAS Mixture in Zebrafish (Danio rerio).Toxics. 2022 Jun 18;10(6):334. doi: 10.3390/toxics10060334. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35736942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarabi M, Qin Z, Xu W, Mewburn J, Oko R. Sperm-borne protein, PAWP, initiates zygotic development in Xenopus laevis by eliciting intracellular calcium release. Mol. Repro Dev. 2010;77:249–256. - PubMed
-
- Begley MJ, Taylor GS, Kim SA, Veine DM, Dixon JE, Stuckey JA. Crystal structure of a phosphoinositide phosphatase, MTMR2: insights into myotubular myopathy and Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1391–402. - PubMed
-
- Blum M, De Robertis EM, Wallingford JB, Niehrs C. Morpholinos: Antisense and sensibility. Dev. Cell. 2015;35:145–149. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

